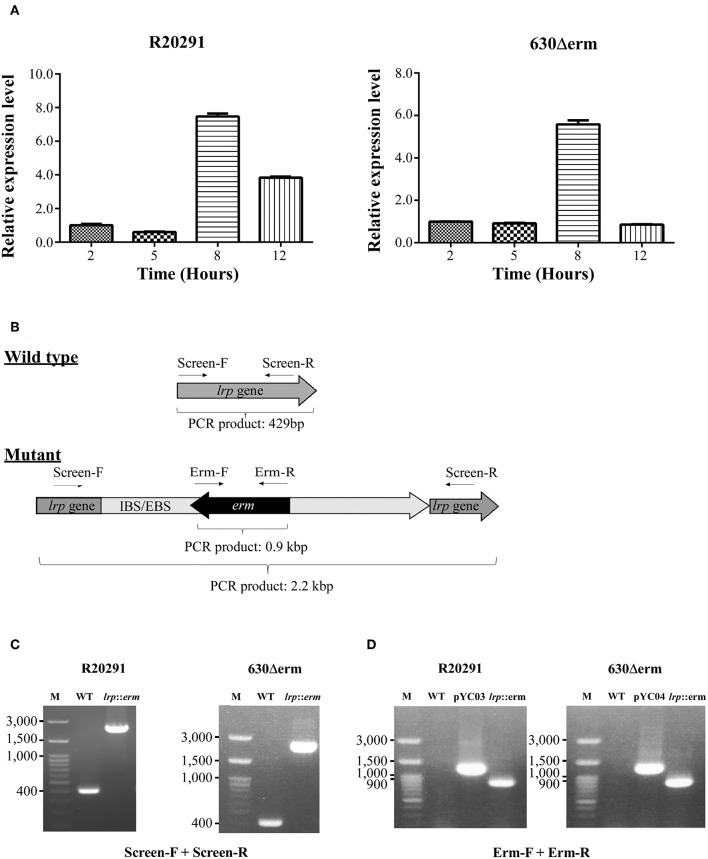
Figure 2.
Growth phase–dependent lrp transcriptional profiling and insertional inactivation of lrp in C. difficile R20291 and 630Δerm. (A) lrp transcript level at different time interval representing various growth phases in BHIS were studied: 2 h (lag phase), 5 h (early log phase), 8 h (mid-log phase), and 12 h (late log/early stationary phase). (B) An illustration of ClosTron-dependent insertional mutation and primers used. The ClosTron delivery system is encoded on plasmid and consists of a group II intron with an internal retro-transposition-activated marker conferring erythromycin resistance. The group II intron is re-targeted to the desired target gene by altering the sequence of the intron-binding site/exon-binding site region using overlapping PCR. This results in the splicing of the group II intron into the target gene. The locations of primers used to screen for potential mutant are indicated. (C) PCR confirmation using primers Lrp-screen-F and Lrp-screen-R. (D) Insertion confirmation using primers Erm-F and Erm-R. M, DNA ladder; WT, wild type; pYC03, R20291 lrp ClosTron plasmid; pYC04, 630Δerm lrp ClosTron plasmid; lrp, erm: lrp mutant.