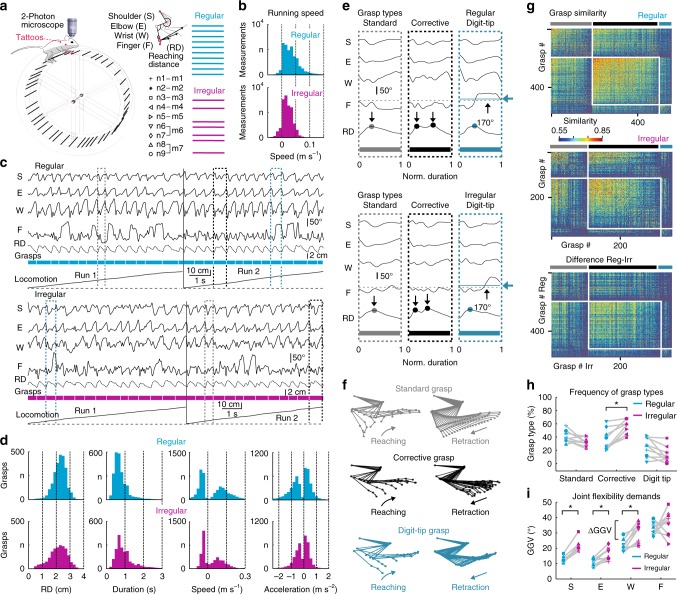
Fig. 1.
Analysis of forelimb grasps and running behavior on ladder wheels. a Setup with head-fixed mouse on top of a ladder wheel and below a two-photon microscope. Joint angle changes in shoulder (S), elbow (E), wrist (W), and finger base (F), as well as the reaching distance (RD), were quantified by tracking tattoos on the right forelimb (red dots). Nine neuronal networks in M1 L2/3 (n1–n9) were recorded from seven mice (m1–m7) while they moved across rungs with regular (cyan) or irregular (magenta) spacing. b Running speed histograms, pooled for all mice on the regular (cyan) and irregular (magenta) wheel. c Time course of forelimb joint angles and RD during two runs on regular (top) and irregular (bottom) rungs. Three prototypical grasps are highlighted: Standard (gray), corrective (black), and digit-tip grasp (dark turquois). d Histograms of maximal RD during each grasp, grasp duration, mean grasping speed during paw reaching/retraction (positive/negative values), and mean grasping acceleration during reaching/retraction (positive/negative values) for both conditions, pooled across all seven mice. e Kinematic profile of joint angles and RD for standard (gray), corrective (black), and digit-tip (dark turquois) grasps during both conditions (grasps marked in (c) with duration normalized). Dots on RD traces indicate the number of reaching cycles during the grasp; black horizontal dashed lines mark 170° threshold for mean finger extension, which is exceeded only in digit-tip grasps as indicated by the dark turquois line and arrow). Time scale is normalized from start (0) to end (1) of grasps. f Representative stick-figure plots of limb kinematics for the three principal grasp types. g Grasp-similarity matrices of one mouse for the regular and irregular condition as well as for the difference between both conditions, sorted according to the classification in standard (gray), corrective (black), and digit-tip (dark turquois) grasps and sub-sorted according to similarity values. h Fraction of grasps types on the regular and irregular wheel for all nine neuronal networks. i Grasp-to-grasp variability (GGV) of each joint on the regular and irregular pattern for all nine neuronal networks; h, i: Asterisks indicate P < 0.05 (paired t-test, P-value adjusted according to Holm–Bonferroni)