Figure 2.
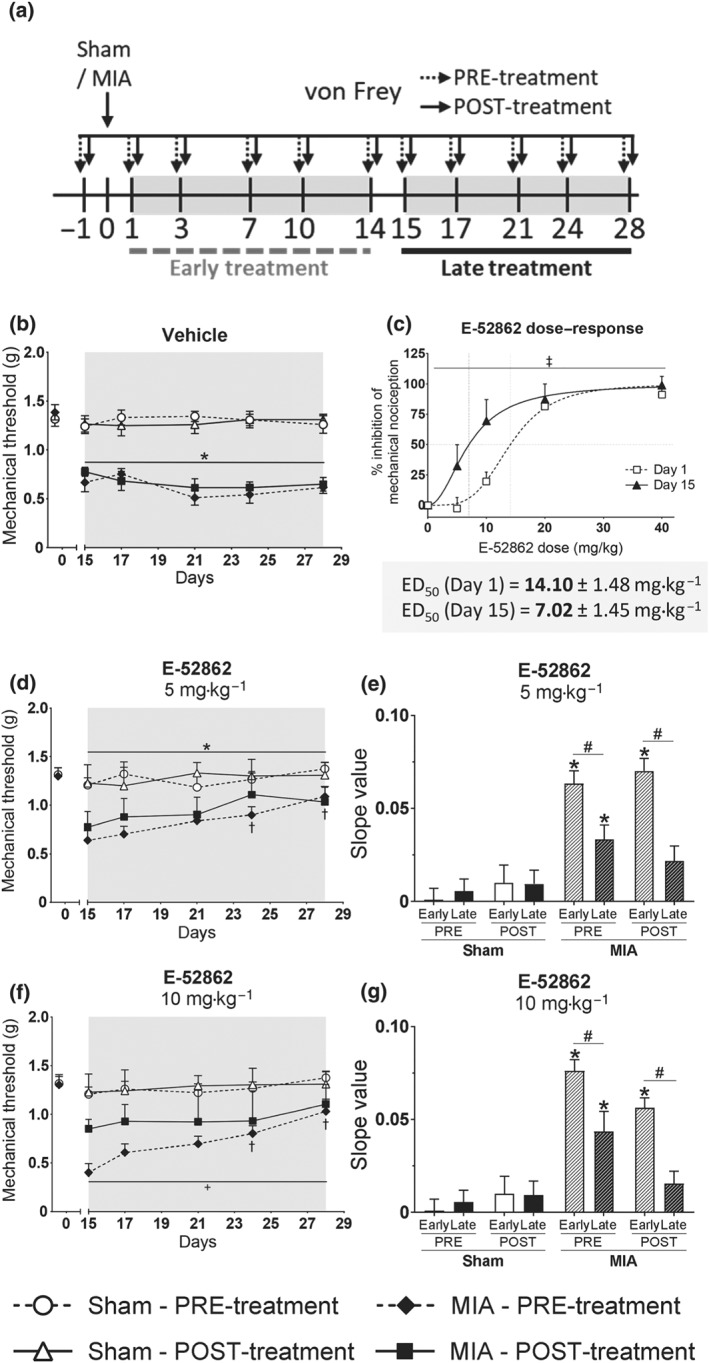
Acute and repeated E‐52862 treatments starting 1 or 15 days after MIA injection differ in their analgesic efficacy. (a) The analgesic effects of acute and chronic E‐52862 (5 or 10 mg·kg−1, twice a day during 14 days) were compared between treatments starting 1 (early) or 15 (late) days after the injection of MIA. (b) MIA‐induced sensitization was stable in vehicle‐treated mice from Day 15 to Day 28 after intra‐knee injection. (c) Lower doses were needed to induce acute relief of mechanical hypersensitivity 15 days than 1 day after the intra‐knee injection of MIA. Mice receiving chronic late treatments with E‐52862 5 mg·kg−1 (d) and 10 mg·kg−1 (f) also showed a recovery of the mechanical thresholds. (e,g) The restoration of mechanical sensitivity was slower in the late than in the early treatment protocol, as reflected on reduced slopes of the time‐course curves of mechanical allodynia. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. The number of animals is the following (first value represents Day 1 or sham groups and second value represents Day 15 or MIA groups): (b) 9, 8; (c) 10, 8; and (d) 8, 8; (f) 8, 8. For panels (b) and (d–g), *P<.05, significant difference between MIA and Sham; †P<.05, significant difference between MIA and MIA at Day 1; + for MIA‐PRE versus MIA‐POST (three‐way repeated measures ANOVA plus Fisher least significant difference test). For panel (c), ‡P<.05, significant difference between Day 1 and Day 15 (F test of non‐linear regression). ED50, median effective dose; MIA, monoiodoacetate
