Figure 5.
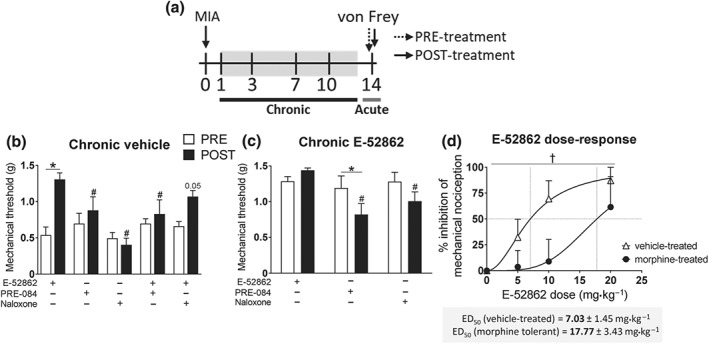
Participation of μ receptors in the antiallodynic effect of E‐52862. (a) Osteoarthritic mice were treated with vehicle (0.5% HPMC), E‐52862 (20 mg·kg−1), or morphine (2.5 mg·kg−1, twice a day during 14 days). In the last day of treatment, mice received acute doses of E‐52862 (5–20 mg·kg−1), PRE‐084 (32 mg·kg−1), naloxone (1 mg·kg−1), or combinations of these drugs. (b) Acute E‐52862 (20 mg·kg−1) showed reduced anti‐allodynic effect when co‐administered with PRE‐084 and a trend towards a decreased antinociception when given together with naloxone. (c) Once mechanical allodynia was normalized after chronic E‐52862, acute administration of PRE‐084 and naloxone induced reduction of the mechanical thresholds. (d) E‐52862 administered to morphine‐tolerant mice showed reduced antinociceptive effects. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. The number of animals is the following: (b) 6 per group; (c) 6 per group; (d) 8 for vehicle‐treated, 6 for morphine‐treated. For panels (b) and (c): *P<.05, significant difference between PRE and POST; # P<.05, significant difference from E‐52862 POST (two‐way repeated measures ANOVA plus Fisher least significant difference test). For panel (d): † P<.05, significant difference between vehicle‐treated and morphine‐treated (F test of non‐linear regression). MIA, monoiodoacetate. †
