Figure 7.
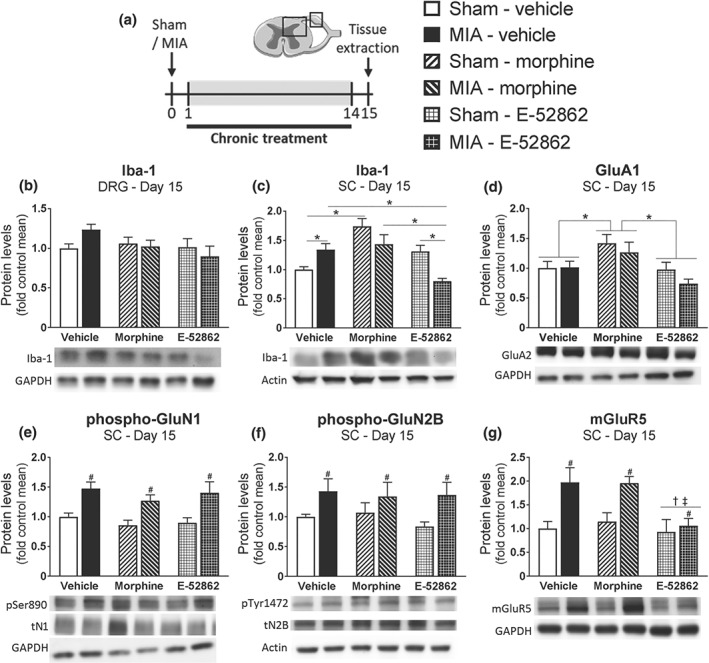
Repeated treatment with E‐52862 decreases pain‐induced microgliosis and mGluR5 up‐regulation. (a) Fifteen days after sham or MIA injection, spinal cord, and DRG were extracted from vehicle‐ (0.5% HPMC), morphine‐ (2.5 mg·kg−1), or E‐52862‐ (20 mg·kg−1) treated mice. (b) Protein levels of Iba‐1 showed no significant differences in the DRG. (c) At spinal level, Iba‐1 was increased after MIA or chronic morphine and reduced by E‐52862. (d) Morphine induced an up‐regulation of GluA2 AMPA receptor subunit. Phosphorylation levels of GluN1 (e) and GluN2B subunits (f) of the NMDA receptor were increased after MIA injection regardless of the treatment received. (g) MIA injection significantly increased the protein levels of mGlu5, which were reduced after E‐52862. GAPDH or actin was used as a housekeeping control. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. The number of animals is 6 per group. #P <.05, significant difference between MIA and sham; †P <.05, significant difference between E‐52862 and vehicle; ‡P <.05, significant difference between E‐52862 and morphine; *P <.05, significantly different as indicated; two‐way ANOVA followed by Fisher least significant difference test: MIA, monoiodoacetate; SC, spinal cord; DRG, dorsal root ganglia; pSer890, phosphorylation of Ser890 of the N1 subunit of the NMDA receptor; tN1, total N1 subunit; pTyr1472, phosphorylation of Tyr1472 of the N2B subunit of the NMDA receptor; tN2B, total N2B subunit
