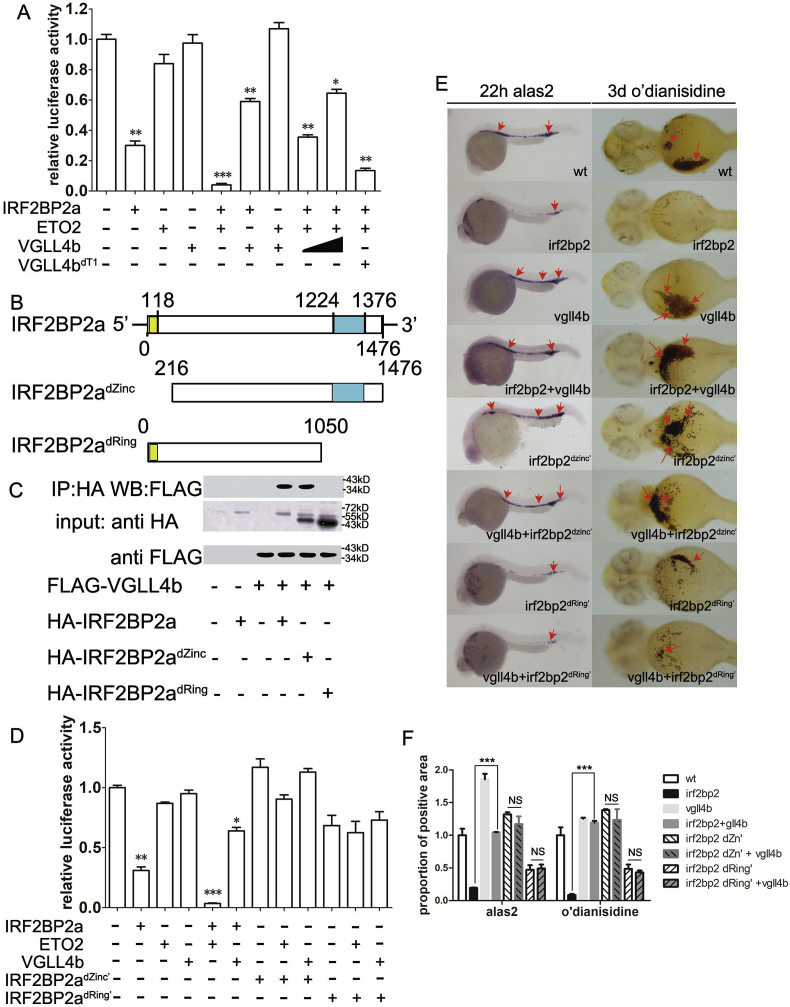
Fig. 6.
Mechanism underlying VGLL4b interference with the suppressive effect of IRF2BP2 on erythroid terminal differentiation. (A) Luciferase assays demonstrating the effects of IRF2BP2a, ETO2 and VGLL4b in regulating alas2 expression. Neither ETO2 nor VGLL4b alone influenced alas2 expression; however, they induced and reduced suppression via IRF2BP2a. (B) Construction of the IRF2BP2a mutants, IRF2BP2adZinc’ and IRF2BP2adRing’. (C) Co-IP assay demonstrating that interaction of VGLL4b and IRF2BP2a depends on the ring finger domain and its surrounding region. (D) Luciferase assays using IRF2BP2a mutants. Neither IRF2BP2adZinc’ nor IRF2BP2adRing’ influenced the effects of ETO2 or VGLL4b on alas2 expression. (E and F) Biological effects of IRF2BP2a mutants on heme biosynthesis suppression and VGLL4 function. IRF2BP2adZinc’ was unable to repress heme biosynthesis, while IRF2BP2adRing’ was partially effective. Both mutants prevented the rescue effect of VGLL4 on heme biosynthesis. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM of at least 15 to 30 embryos in each subgroup. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. NS denotes no significant difference.