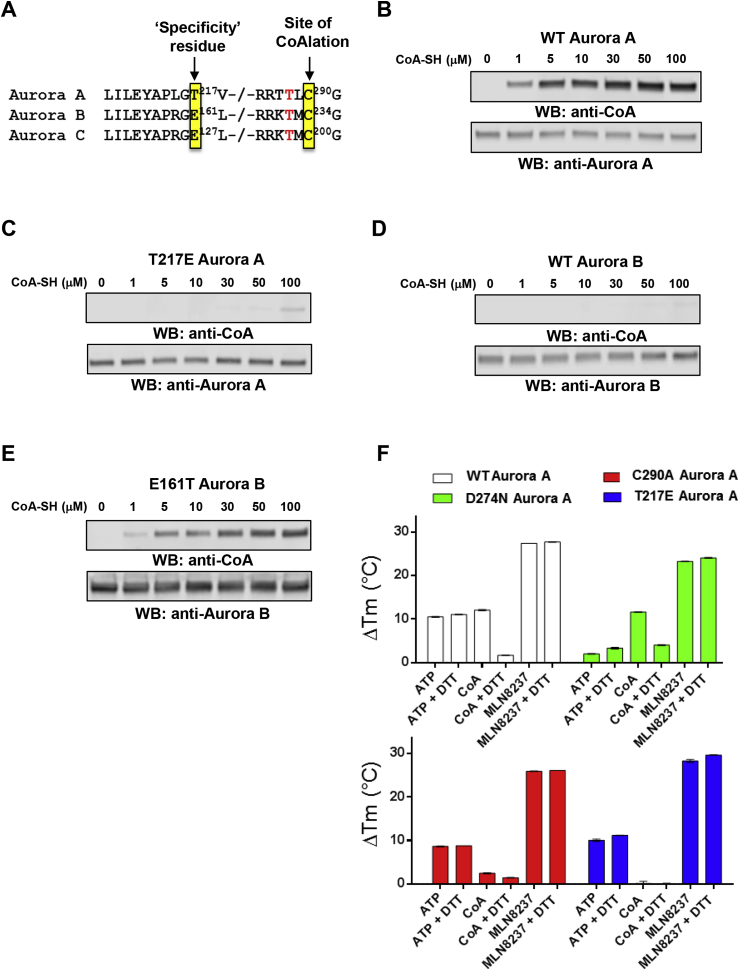
Fig. 3.
Specificity of Aurora A interaction with CoA is controlled by Thr 217.(A) Amino acid conservation in vertebrate Aurora kinases. Thr 217 defines Aurora A, and is changed to a Glu residue in Aurora B and C. Cys 290 (boxed) is invariant in all Aurora kinases, and lies in the activation segment adjacent to the phosphorylated Thr 288 (human Aurora A numbering). (B)In vitro CoAlation of Aurora A. (C)In vitro CoAlation of Aurora A is abolished in the Thr217Glu mutant. (D)In vitro CoAlation is not detected with Aurora B. (E) The Glu161Thr Aurora B mutant is efficiently CoAlated. Experiments were performed with the indicated concentration of CoA. Reaction mixtures were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-CoA, Aurora A or Aurora B antibodies. (F) A thermal shift assay was employed to evaluate Aurora A binding to 5 mM ATP, 5 mM CoA or 0.1 mM MLN8237, in the presence and absence of 1 mM DTT, as indicated. Assays were performed with T 288 phosphorylated, active, Aurora A (open bars), kinase-dead, dephosphorylated Aurora A (Asp274Asn, green bars), Cys290Ala Aurora A (red bars) or Thr217Glu Aurora A (blue bars). Mean ΔTm values ± SD (n = 3) were calculated by subtracting the control Tm value (buffer, no addition) from the measured Tm value. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)