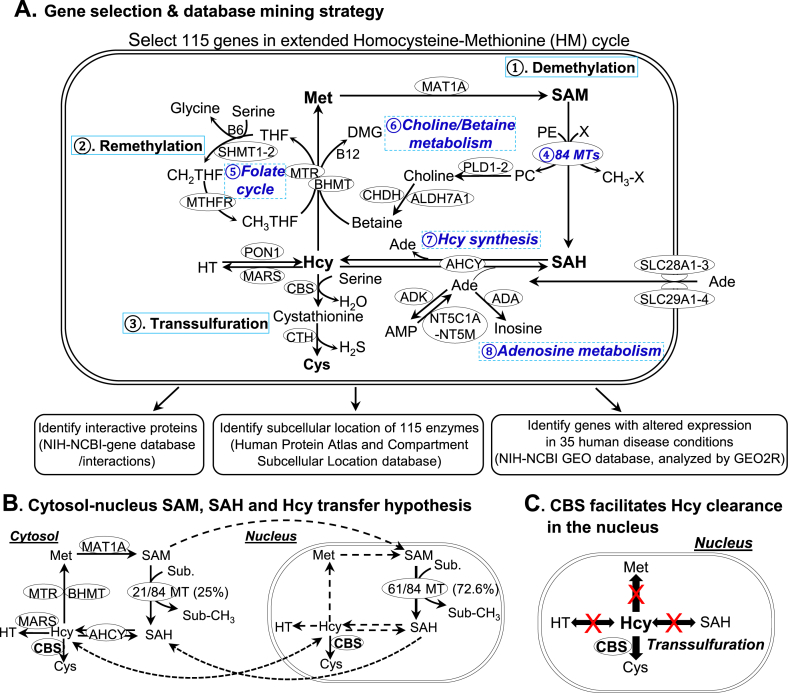
Fig. 1.
HM cycle senses metabolic risk factors and modulates SAM/SAH-dependent methylation and pathogenic signaling. A. Extended HM cycle, gene selection & database mining strategy. We selected 115 genes in this cycle from Human metabolome database (https://www.hmdb.ca/). The HM cycle includes 3 major pathways. ① Demethylation pathway: Met is converted to SAM, which becomes SAH after donating the methyl group for cellular methylation. SAH is then converted to Hcy, a dual directional reaction, interacting with adenosine metabolism. ② Remethylation pathway: Hcy is converted back to Met by regaining the methyl group from folate cycle or choline/betaine metabolism. ③ Transsulfuration pathway: Hcy is converted to Cys. The extended HM cycle includes additional pathways, such as ④ 84 MTs, ⑤ folate cycle, ⑥ choline/betaine metabolism, ⑦ Hcy synthesis and ⑧ adenosine metabolism. These 115 genes’ mRNA levels in human disease conditions were analyzed by mining NIH-NCBI GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/), protein subcellular localization and interacting partner were identified by using information in Human Protein Atlas (https://www.proteinatlas.org/), compartment subcellular location database (https://compartments.jensenlab.org) and NIH-NCBI gene database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene), respectively. B. Cytosol-nucleus SAM, SAH and Hcy transfer hypothesis. All essential enzymes in the HM metabolic cycle are located in the cytosol, only 21 out of 84 MTs (25%) in the cytosol but the majority of MTs (72.6%) in the nucleus. Some of the HM cycle metabolic processes are not active in the nucleus because their metabolic enzymes are not identified there and indicated by dash lines. For example, enzymes for SAM synthesis, SAH clearance and Hcy synthesis are missing in the nucleus. C. CBS facilitates Hcy clearance in the nucleus. Since only one Hcy clearance enzyme exists in the nucleus, we propose that CBS facilitates Hcy clearance in the nucleus. Abbreviations: Ade, adenosine; Hcy, homocysteine; SAM, S-Adenosylmethionine; SAH, S-Adenosylhomocysteine; Met, Methionine; MTs, Methyltransferase; CBS, Cystathionine-β-synthase; HT, homocysteine thiolactone. Abbreviations for gene and enzyme names are explained in Supplementary Table 1.