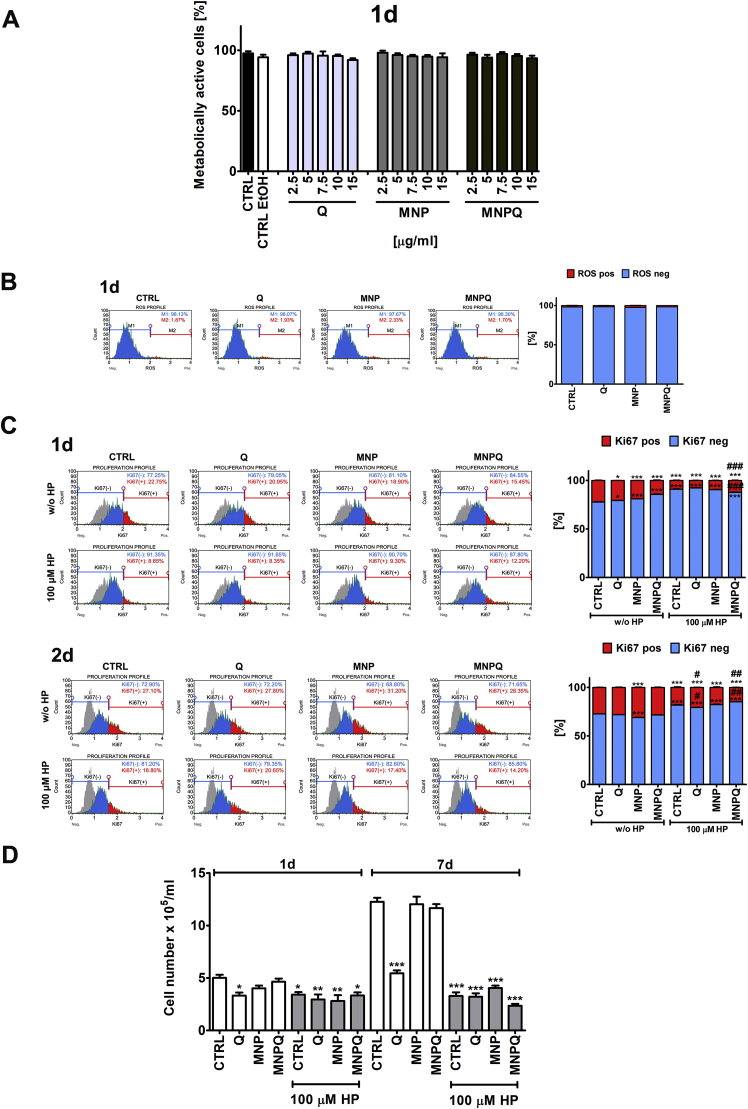
Fig. 2.
MNPQ-mediated effects on cell proliferation during hydrogen peroxide-induced senescence in BJ human fibroblasts. The concentrations of Q, MNP and MNPQ were selected on the basis of MTT results (A) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (B) upon 24 h stimulation with Q, MNP or MNPQ (2.5 to 15 μg/ml). A concentration of 5 μg/ml that did not promote changes in metabolic activity and ROS production was selected for further analysis. (A) The metabolic activity was analyzed using MTT test. Metabolic activity at control conditions (CTRL) is considered as 100%. A solvent action (ethanol) is also shown. (B) Superoxide levels were measured using Muse™ Cell Analyzer and Muse™ Oxidative Stress Kit. Representative histograms are presented. Cell proliferation was measured using Ki67 immunostaining (C) and cell count analysis (D). Cells were stimulated with 100 μM hydrogen peroxide (HP) for 2 h and then cultured in the presence of 5 μg/ml Q, MNP or MNPQ for 24 h, and then culture for up to 168 h without Q, MNP or MNPQ. (C) Cell proliferation was assayed using Muse™ Cell Analyzer and Muse™ Ki67 Proliferation Kit. Representative histograms are presented. A negative control without incubation with Ki67 specific antibody is denoted as a grey histogram in each studied sample. Ki67 immunostaining was analyzed after 24 h treatment with 5 μg/ml Q, MNP or MNPQ. (D) Cell number was analyzed using TC10™ automated cell counter. Bars indicate SD, n = 3, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 compared to CTRL, ###p < 0.001, ##p < 0.01, #p < 0.05 compared to HP-treated control (ANOVA and Dunnett's a posteriori test). CTRL, control conditions; Q, quercetin; MNP, magnetite nanoparticles; MNPQ, quercetin surface functionalized magnetite nanoparticles.