Figure 3.
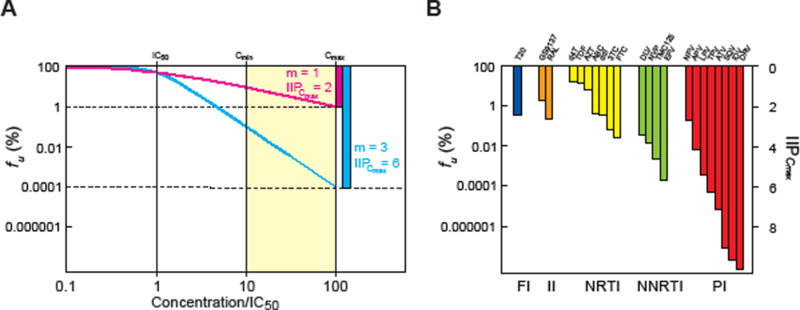
Clinical concentrations of some antiretroviral drugs cause profound inhibition of viral replication as a result of high slope values. (A) Hypothetical dose-response curves for two antiviral drugs with the same IC50 but different slope values. The response is plotted as fu, the percent of infection events that are unaffected by a given concentration of drug. For drugs with an m value of 1, the dose-response curves are shallow, and the degree of inhibition achieved in the clinical concentration range (shaded area, 10–100 times the IC50) is limited. For a drug with an m value of 3 and the same IC50, 10,000 fold greater inhibition is achieved at Cmax. (B) IIP of current antiretroviral drugs at Cmax plotted on the same scale as in (A). Note that for some PIs, IIP is on the order of 10 logs, a 10,000,000,000 fold inhibition of replication.
