Figure 2. TNF-Tg lungs have a restrictive pulmonary pathology.
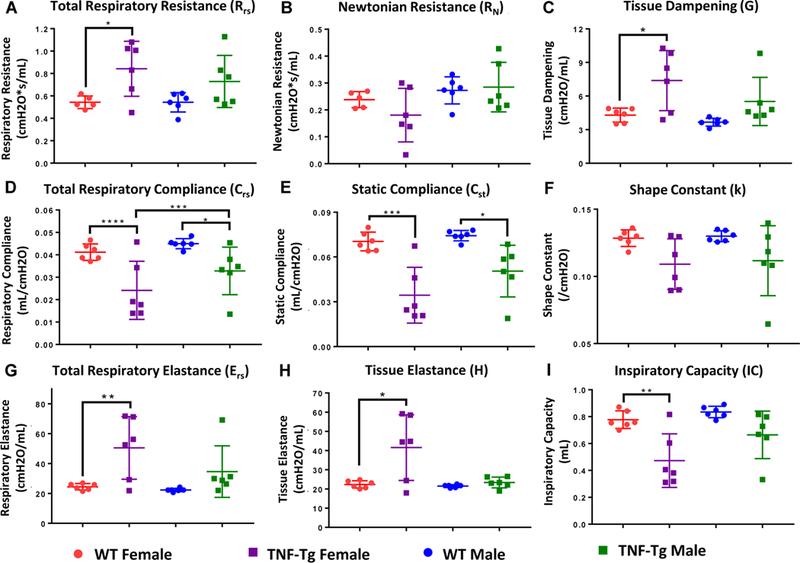
The mice described in Figure 1 underwent forced pulmonary manipulation as described in Materials and Methods. 2-way ANOVAs with Sidak’s post hoc multiple comparisons were used to analyze differences in mechanical parameters between cohorts. Data for mechanical parameters: (A) total respiratory resistance, (B) Newtonian resistance, (C) tissue dampening, (D) total respiratory compliance, (E) static compliance, (F) the shape constant, (G) total respiratory elastance, (H) and tissue elastance, are presented for individual mice with mean +/− SD (n=6, *p>0.05,**p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001). Note that within sex, differences between TNF-Tg and WT mice were found for multiple parameters measuring tissue “stiffness”, including total respiratory resistance, tissue dampening, total respiratory compliance, static compliance, total respiratory elastance, and tissue elastance. Between the sexes, female TNF-Tg mice consistently trended towards increased disease severity compared to their male counterparts over multiple measures, yet only respiratory compliance reached statistical significance.
