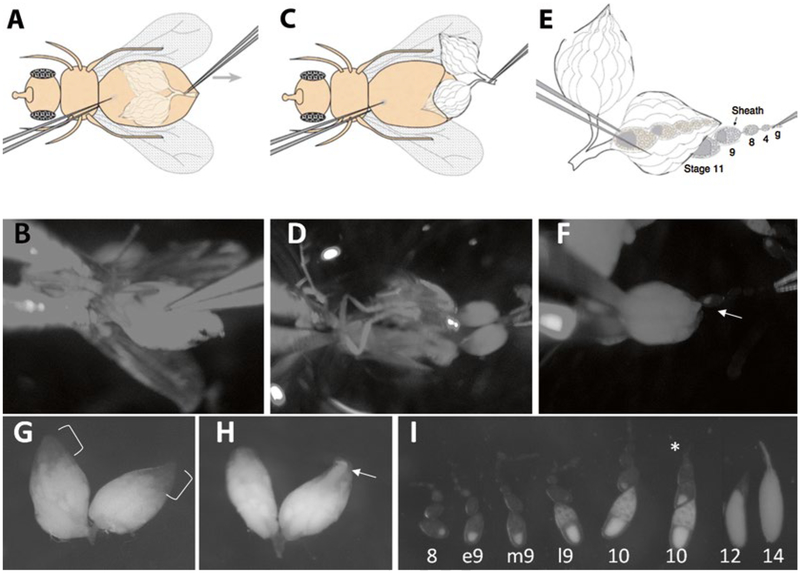
Fig. 3.
Dissection of stage 9 egg chambers. (a and b) Hold the fly body and pinch the abdominal cuticle. (c and d) Pull until the ovaries come out. (e and f) Pull ovarioles out of muscle sheath. Arrow points to a stage 9 egg chamber emerging from the ovary. (g) In well-fattened ovaries, the anterior 1/3 of the volume of the ovaries should be composed of young egg chambers, which are not as opaque as mature eggs (bracket). (h) III-fattened ovaries are usually smaller, have less early-stage egg chambers, and have more mature egg chambers sometimes in the anterior tip of the ovary (arrow). (i) Different stage egg chambers. Stage 9 is characterized by the size of the egg chamber, outer follicle cell arrangement, oocyte proportion, and the amount of yolk deposits in the germ cells. Asterisk points to an ovariole that remains in muscle sheath