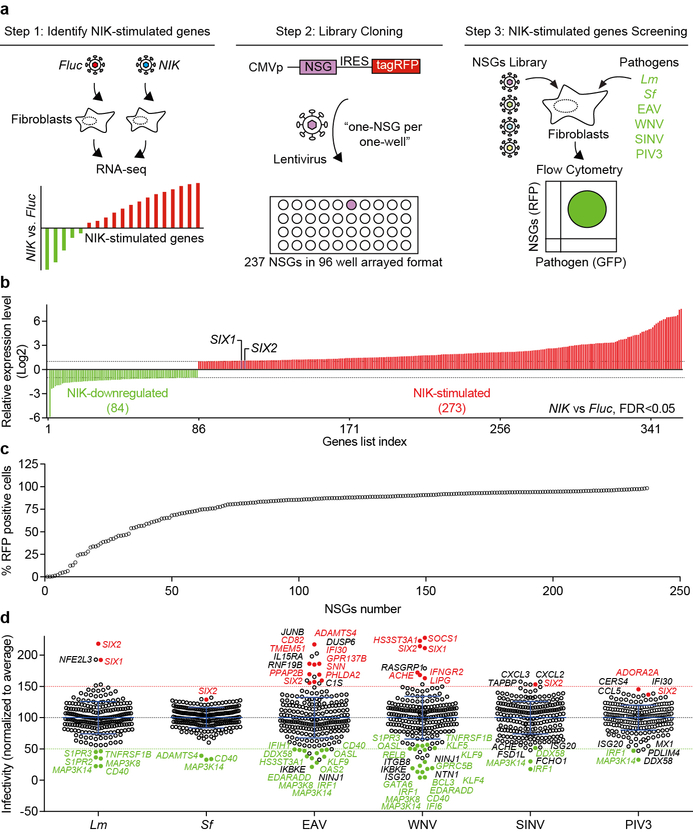
Extended Data Fig. 2. NIK-stimulated genes library screen.
a, Schematic of NIK-stimulated gene library design, cloning, and the multidimensional flow cytometry based high throughput screen. NIK-stimulated genes were determined by RNA-seq. The cDNAs of 237 NIK-stimulated genes were individually cloned into the lentiviral vector pTRIP upstream of the IRES-tagRFP (see methods). Fibroblasts were transduced with lentivirus in a one-gene to one-well format and were then infected with GFP expressing Lm, Sf, EAV, WNV, SINV, and PIV3 in independent experiments. The effect of a single gene expression on infection was quantified by flow cytometry. b, The relative expression levels of NIK-stimulated genes identified by RNA-seq. Fluc or NIK lentivirus was transduced into fibroblasts. Total RNA was isolated after 72 hours and gene expression level was determined by RNA sequencing. Graph shows gene expression levels that are significantly stimulated (red, 237 genes) or downregulated (green, 84 genes) by NIK expression compared to Fluc control. Fold change over 2 (Log2≥1) or less 0.5 (Log2≤−1) and FDR<0.05 (statistics test is presented in methods section). Bars were ranked numerically from low to high (see Table S1 for details). The expression levels of SIX1 and SIX2 are indicated. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. c, Graph showing the efficiency of lentiviral expression of NIK-stimulated genes used in the high throughput bacterial and viral screen. NIK-stimulated genes were transduced into WT fibroblasts in a “one-gene per one-well” format. Transduction efficiency as measured % RFP positive cells was determined by flow cytometry and was ranked numerically from low to high (see source data for details, values are from the average of 2 technical replicates). 12 out of 237 genes were poorly transduced (less than 20% RFP+) and were excluded from subsequent analyses. d, Dot plots of Sf, Lm, EAV, WNV, SINV, and PIV3 infectivity in the presence of expressed NIK-stimulated genes (in c). Data were normalized to the average of each screen, indicating as the black dotted line. We chose to confirm hits in Fig. 1d based on two criteria: (1) the gene expression effect on inhibiting or enhancing pathogen infection by less than or greater than 50%, and (2) an adjusted Z-score less than −2 or greater than 2 (see Table S2 for details). NIK-stimulated genes that reproducibly and significantly inhibited (green) or enhanced infection (red) by these criteria are indicated. The genes shown in black font are hits that were not reproduced in the confirmatory experiments (Fig. 1d). Data are mean±s.d. from 2 (Sf and Lm) or 1 (EAV, WNV, SINV, and PIV3) independent experiments.