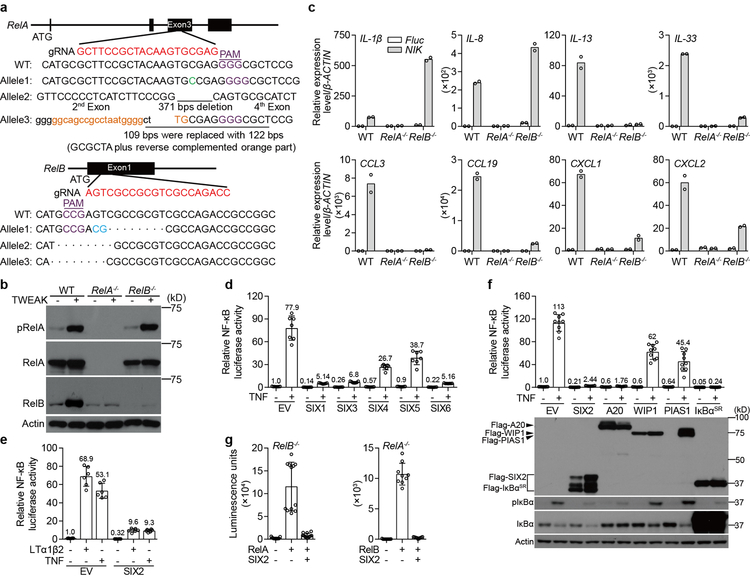
Extended Data Fig. 5. SIX-family proteins inhibit RelA and RelB mediated NF-κB activation.
a, b, Characterization of RelA−/− and RelB−/− in human fibroblasts. Schematic representation of In/Del base pairing and the sgRNA targeting locus of Exon 3 in RelA and Exon 1 in RelB gene. RelA−/− cells contain +C, −371 bps, and a 109 bps fragment that was replaced with 122 bps containing the GCGCTA with reverse complementary (orange fragment) (a up). RelB−/− cells contain the indicated deletions (a bottom). Western blot shows endogenous RelA and RelB expression in parental and RelA−/− or RelB−/− fibroblasts and response to stimulation by 24-hour application of TWEAK (b). c, Experiments evaluating the contributions of the canonical and non-canonical NF-κB subunits RelA and RelB, respectively, on expression of the indicated genes. Fluc or NIK was transduced into WT, RelA−/−, and RelB−/− fibroblasts to stimulate the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway and mRNA expression of the indicated genes were evaluated by qRT-PCR. We concluded that the IL-1β gene is specifically stimulated by RelA since we did not detect its expression in RelA−/− cells but did so in RelB−/− cells (which expression RelA). Similar logic was used to evaluate the 7 additional genes shown. Experiments were performed as described in Fig. 2g. Bars are mean of 2 technical replicates (shown as circle) and representative of 2 independent experiments. d, The human SIX-family consists of 6 unique isoforms. To determine which of these genes suppress NF-κB mediated gene expression, empty vector (EV), SIX1, SIX3, SIX4, SIX5, or SIX6 cDNAs were co-transfected with 5×κB-LUC into HEK293T cells. After 24 hours, cells were treated with mock or 25 ng/ml TNF for 24 hours. The luciferase activity was measured and normalized to EV untreated control. SIX1, SIX3, and SIX6 (SIX2 was not evaluated in this experiment) potently inhibited both basal and inducible activity of NF-κB. Data are mean±s.d. from 7 independent experiments. e, SIX2 inhibits LTα1β2- and TNF-induced NF-κB activation. EV or Flag-SIX2 was co-transfected with 5×κB-LUC into WT fibroblasts. After 24 hours, cells were treated with mock, 25 ng/ml TNF or 50 ng/ml LTα1β2 for 24 hours. Data were analyzed as described in d. Data are mean±s.d. from 6 independent experiments. f, The inhibitory potency of SIX2 is equivalent to A20 and IκBαSR. The Flag-tagged genes indicated were co-transfected with 5×κB-LUC into HEK293T cells. After 24 hours, cells were treated with mock or 25 ng/ml TNF for 24 hours. Data were analyzed as in d. Data are mean±s.d. from 9 independent experiments. Anti-Flag western blot was performed to determine expression levels, IκBα regulation was included as pathway activation control upon cellular stimulation with TNF. g, Experiments showing that SIX2 specifically inhibits the activity of both canonical and non-canonical NF-κB isoforms RelA and RelB, respectively. To evaluate the transcriptional activity of each NF-κB isoform independently, we transfected RelA cDNA into RelB−/− cells and RelB cDNA into RelA−/− cells along with SIX2, 5×κB-LUC. Transfection of both RelA and RelB potently induced NF-κB transcription of the indicated cells, and this transcription was suppressed by SIX2. Luminescence units were measured post 48 hours transfection. Data are mean±s.d. from 12 (left) and 9 (right) independent experiments. All western blot data are representative of 3 independent experiments. For gel source data, see Supplementary Figure 1.