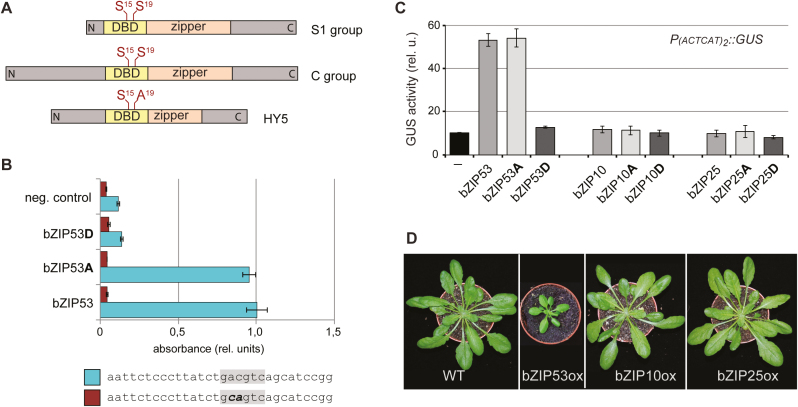
Fig. 1.
Effect of the substitutions of Ser15 and 19 within the DNA-binding domain (DBD) of Arabidopsis bZIP factors on their DNA-binding and transcriptional activity. (A) Schematic representation of bZIP factors. The DBDs and leucine zipper (zipper) domains are indicated. S15 and S19 indicate conserved Ser residues within the DBDs. (B) Binding of bZIP53, bZIP53Ser15,19Ala (bZIP53A), bZIP53Ser15,19Asp (bZIP53D), and unspecific protein (neg. control) to the C-box (lower bars) and mutated C-box (upper bars). Data are means (±SD), n=2. (C) Reporter gene assays in Arabidopsis protoplasts. P(ACTCAT)2x::GUS was used as the reporter. A, substitution of Ser15 and Ser19 to Ala; D, substitution of Ser15 and Ser19 to Asp. Data are means (±SD), n=3. (D) Images of representative plants from each transgenic line expressing PUBI10::bZIP53-GFP (bZIP53ox), P35S::bZIP10-GFP (bZIP10ox), and P35S::bZIP25-GFP (bZIP25ox). (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)