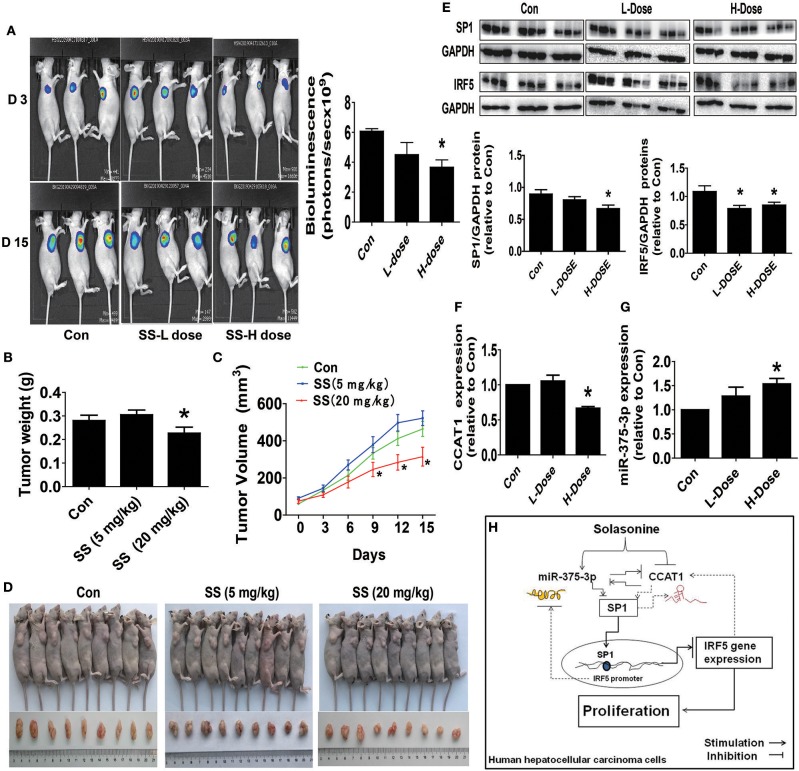
Figure 6.
The anti-HCC effects by SS in a mouse xenograft tumor model. (A) HepG2-Luc cells carrying luciferase reporter gene (HepG2-Luc, obtained from the Guangzhou Land Biological Technology Co., Guangzhou, China) were resuspended in 0.2 mL of phenol red-free RIPM 1640 with 2% FBS in a number of 2.0 × 106. Then, the resuspended cells were injected into the upper hind limb of the nude mice. Xenografts were expected to grow for 1 week when starting the first measurements. Mice were randomly divided into three groups: the control, low-dose group (SS, 5 mg/kg), and high-dose group (SS, 20 mg/kg), and were injected with reference substance or SS once a day via intraperitoneal injection for up to 15 days (n = 9 per group). The xenografts were assessed by in vivo bioluminescence imaging at the first and end of the experiments (on day 2 and 15). The tumor growth was monitored by injecting luciferin in the mice followed by measuring bioluminescence using IVIS Imaging System. Imaging and quantification of signals were controlled by the acquisition and analysis software living image as described in the Materials and Methods section. Representative images are shown. (B,C) The xenografts were harvested on day 15, and the weight (B) and volume (C) of tumors were measured. (D) The photographs of the vehicle- and drugs-treated xenografts derived from nude mice are shown. (E–G) At the end of the experiments, xenograft tumors were isolated from individual animals, and the corresponding lysates were processed and detected miR-375-3p and CCAT1 levels, SP1 and IRF5 protein expressions by qRT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. GAPDH was used as a loading control. The figures are representative cropped gels/blots that have been run under the same experimental conditions. The bar graphs represented the tumor weight and volume of mice results of as mean ± SD. *Indicates the significant difference from the untreated control (p < 0.05). (H) The diagram shows that SS inhibits HCC growth through the reciprocal regulation between the miR-375-3p and lncRNA CCAT1, this result in transcription factor SP1-mediated reduction of IRF5 gene expression. The interactions among miR-375-3p, CCAT1, SP1, and IRF5 axis unveil a novel molecular mechanism underlying the anti-HCC growth by SS.