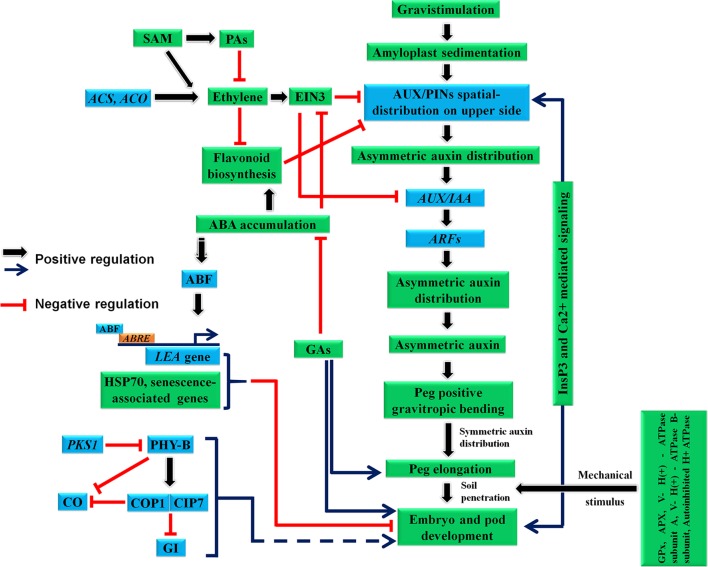
Figure 3.
Probable molecular regulatory mechanism involved during peg development, gravitropic bending, elongation and pod development. ABA, abscisic acid; ABRE, ABA-responsive element; ABF, ABRE-binding factors; ACO, ACC oxidase; ACS, ACC synthase; APX, Cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase; COP1, E3 ubiquitin–protein ligase constitutive photomorphogenic 1; CIP7, COP1-interacting protein 7; CO, constans; EIN3, ethylene-insensitive3; GA, Gibberellic acid; GI, gigantea; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; IM,; LEA, late embryogenesis abundant; PAs, polyamines; PHY-B, phytochrome; PKS1, phytochrome kinase substrate 1; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; V- H(+) - ATPase subunit A, Vacuolar - H(+) - ATPase subunit A; V- H(+) - ATPase B-subunit, Vacuolar - H(+) - ATPase B-subunit.