Fig. 3.
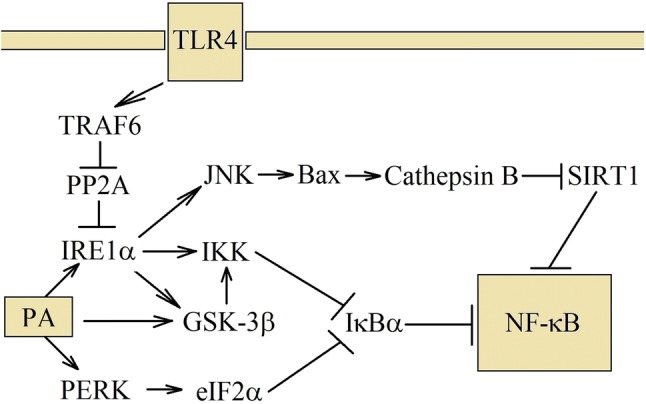
Mechanism of NF-κB activation by PA. PA and TLR4 share some of the signaling pathways. Both activates IRE1α, but in a different way. TLR4 activates this ER stress sensor via TRAF6. In turn, activation through PA depends on the damage of ER membranes and incorporation into them. Then IRE1α activates JNK–MAPK pathway, which destabilizes the lysosomes. Cathepsin B is released, which is involved in the NF-κB activation. IRE1α also activates IKK, which participates in the canonical activation of NF-κB. PA can also cause activation of PERK, which inhibits translation and thereby reduces the level of IκBα that leads, as well, to the NF-κB activation
