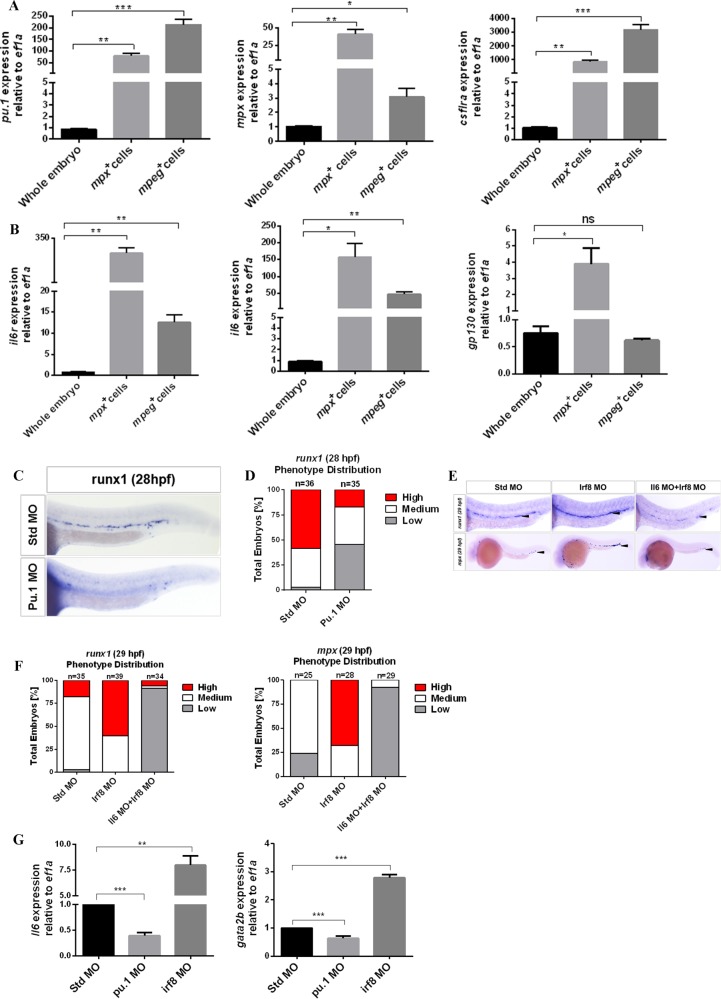
Fig. 5. HSC-independent neutrophils play a key role in HSC specification.
a, b qPCR for detecting the expression of genes, including pu.1, csf1ra, mpx, il6r, il6, and gp130, from purified HSC-independent macrophages (mpeg1:GFP+) and neutrophils (mpx:GFP+) at 30 hpf. Expression was normalized to ef1a and is presented relative to whole-embryo expression. Bars represent the means ± SEM of duplicate samples. *P < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; n.s., not significant. c Std and Pu.1 morphants were examined by WISH for runx1 expression at 28 hpf. d Qualitative phenotype distribution of embryos from c scored with medium, high, and low runx1 expression. Medium, white bar; high, red bar; low, gray bar. e Std, Irf8, and Il6 + Irf8 morphants were examined by WISH for runx1 and mpx at 29 hpf. Black arrowheads denote runx1+ HSCs in the DA region and mpx+ neutrophils in the PBI and trunk regions. f Qualitative phenotype distribution of embryos from e scored as in d. g Whole-embryo expression of il6 and gata2b relative to ef1a in Std, Pu.1, and Irf8 morphants at 28 hpf. Bars represent the means ± SEM of duplicate samples. **P < 0.01; ***p < 0.001