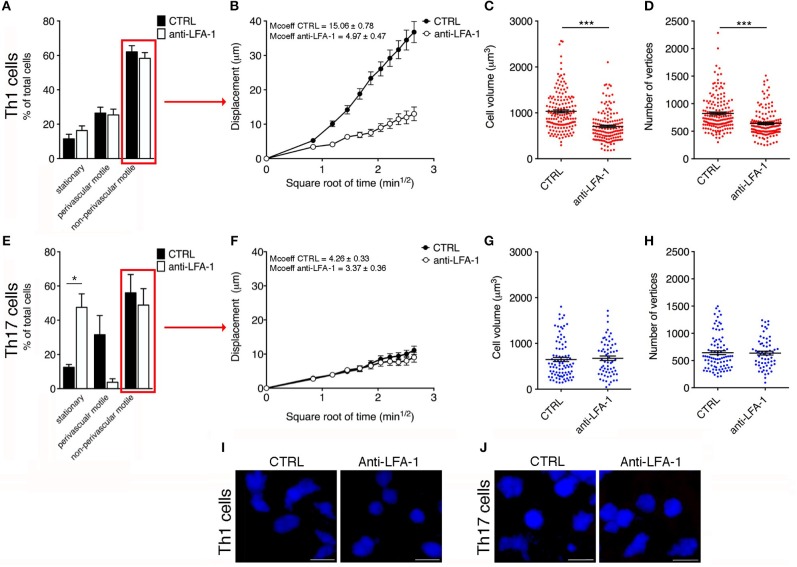
Figure 7.
Blocking LFA-1 specifically affects non-perivascular motile Th1 cell dynamics and cell deformability in the SAS at the EAE disease peak. (A) Dynamic properties of Th1 subpopulations are not affected by blocking LFA-1. (B) Mean displacement of non-perivascular motile Th1 cells is reduced by a LFA-1 blockade. The volume (C) and number of vertices (D) of non-perivascular motile Th1 cells differ before (CTRL) and after the inhibition of LFA-1 (***P < 0.0001). (E) The dynamic properties of the Th17 population: the number of perivascular motile Th17 cells is reduced following the application of an anti-LFA-1 antibody (*P < 0.05). (F) Mean displacement of non-perivascular motile Th17 cells in the tissue is not affected after antibody treatment. The volume (G) and number of vertices (H) of non-perivascular motile Th17 cells do not change after LFA-1 inhibition. (I) Representative images of non-perivascular motile Th1 cells before and after anti-LFA-1 treatment. Note the presence of highly-polarized cells before antibody application (left panel) and the predominant rounded cell morphology induced by blocking LFA-1 (right panel) (scale bar = 15 μm). (J) Blocking LFA-1 had no effect on non-perivascular motile Th17 cell cytoskeletal organization, compared to controls (scale bar = 15 μm). (B,F) Data represent the mean ± SEM of 100 cells from three independent experiments. (C,D,G,H) Data represent the mean ± SEM of 200 cells from three independent experiments.