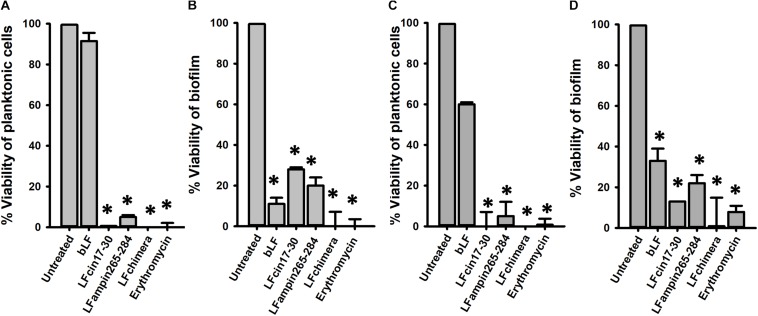
FIGURE 1.
Bovine Lactoferrin and LF-derived peptides inhibit the viability and attachment of pneumococci present in lung cells and supernatants. Human lung cells A549 were inoculated with 7.5 × 104 CFU/ml Streptococcus pneumoniae strain D39 and simultaneously treated with 40 μM bLF, 10 μM LFcin17-30, 10 μM LFampinn265-284, 10 μM LFchimera, and 20 μM Erythromycin. Infected cells were incubated for 4 h (A,B) or 6 h (C,D) at 37°C with 5% CO2. Counts of planktonic pneumococci were obtained in (A,C) while biofilm pneumococci were harvested and counted (B,D). Asterisks indicate statistical significance calculated using the ANOVA t test (p < 0.05). Viable counts of pneumococci in the untreated control were adjusted to 100% and viability on those treated was calculated.