Figure 2.
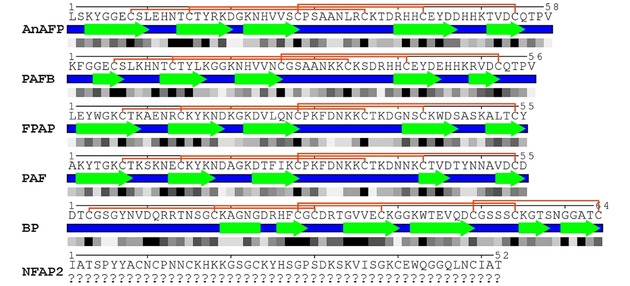
Secondary structure and relative solvent accessibility (RSA) of anti‐yeast crAFPs isolated from Eurotiomycetes. Linear representation of secondary structures and RSA were generated from the respective annotated (PAFB, PAF, BP) or predicted (AnAFP and FPAP) .pdb file of tertiary structure (Protein Data Bank IDs: PAFB‐2nc2, PAF‐2mhv, BP‐1uoy) with POLYVIEW‐2D server39 and revised based on the tertiary structure visualized with UCSF Chimera software.40 Blue lines and green arrows indicate the loop and β‐strand regions, respectively. Connective orange lines between Cys residues indicate disulfide bridge formations. Below the secondary structure, the RSA is indicated, in which the black and white squares represent completely buried (0‐9 RSA) and fully exposed (90‐100 RSA) amino acids, respectively. Putative tertiary structure of AnAFP and FPAP was predicted in silico by I‐Tasser,[41] and refined by ModRefiner.42 Tertiary structure of PAF (Protein Data Bank ID: 2mhv) served as a template to model the structure of AnAFP and FPAP. Question marks indicate that the secondary structure of NFAP2 is under investigation.
