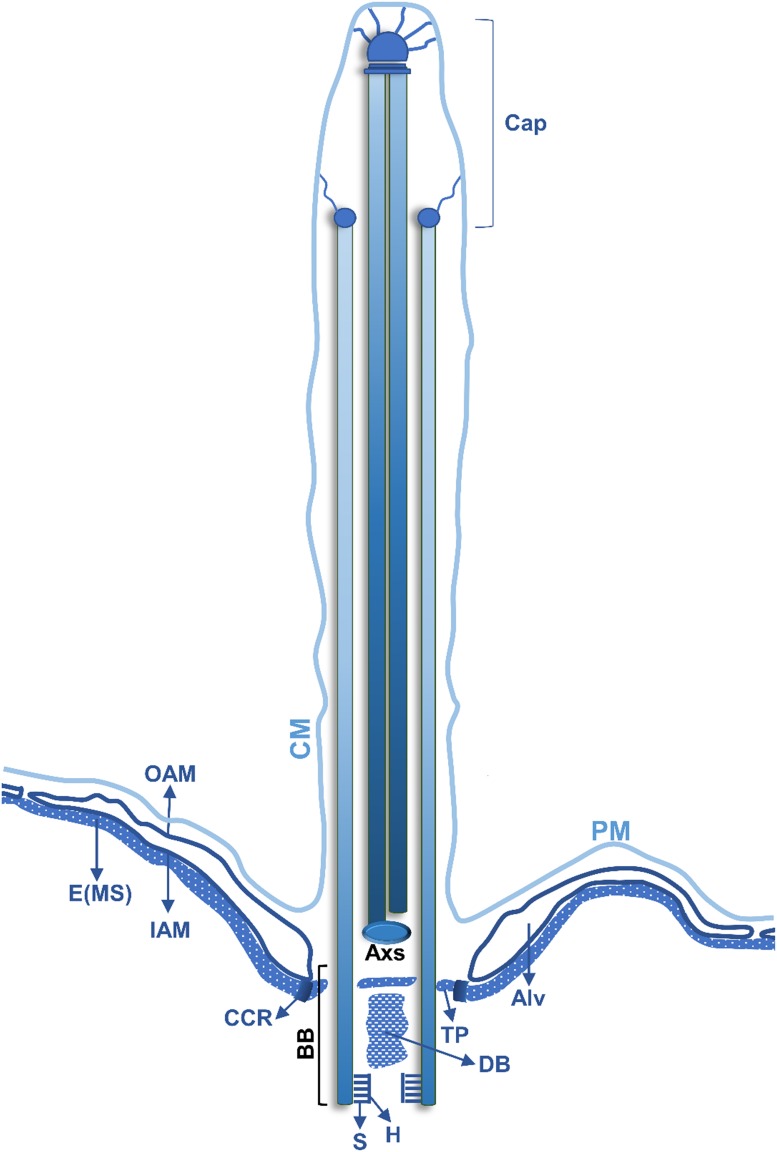
FIGURE 3.
Schematic representation of a longitudinal section of a Tetrahymena somatic cilia. The juxtaposed layers constituted by the plasma membrane (PM), in continuity with the ciliary membrane (CM), alveolus (Alv) and the epiplasm (E) are indicated (see text for details). The outer alveolar membrane (OAM) and the inner alveolar membrane (IAM) surround the Alv. In the BB different structures are indicated: the hub (H) and spokes (S) of the cartwheel structure, a dense body (DB) and the terminal plate (TP). A circumciliary ring (CCR) between the TP and the MS. The peripheral MTs (P) of the axoneme are in continuity with 18 of the 27 MTs of the BB. One MT of the central pair MTs (C) of the cilium originates at the axosome (Axs) at the base of the cilium, while the other originates slightly above the Axs. Toward the distal end, the Tetrahymena cilia axoneme loses the (9 + 2) pattern, and the peripheral MT doublets become singlets. The singlets maintain a circular positioning and are attached to the cilia membrane through filaments that terminate in plug like structures that are inserted in their lumen. The central MT pair is present until the end of the cilia tip and terminates in a complex cap structure (central MT cap), which also links them to the cilia membrane (adapted from Frankel, 2000).