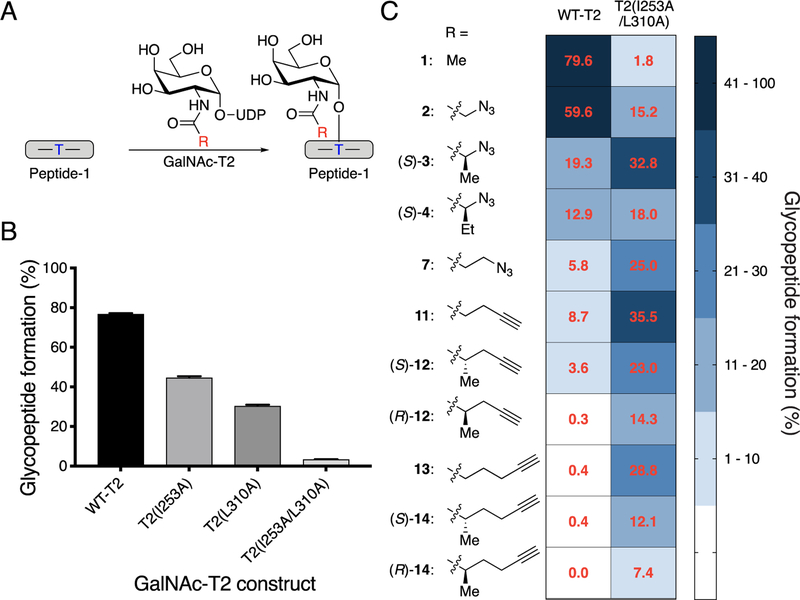
Figure 3.
Screening GalNAc-T2 for an orthogonal enzyme−substrate pair. (A) Scheme for glycosylation reaction with Peptide-1, GalNAc-T2, and UDP-GalNAc or UDP-GalNAc analog to form glycosylated Peptide-1. Blue T indicates the Thr glycosylation site used by GalNAc-T2. (B) Glycopeptide formation by wild-type and mutant GalNAc-T2. UDP-GalNAc and Peptide-1 were incubated with GalNAc-T2 at 37 °C for 1 h, and reaction was quenched by addition of aqueous EDTA (150 mM, pH = 8.0). Percent conversion to glycopeptide product was quantified by HPLC separation and peak integration. All data represent the mean of technical triplicates, and error bars represent the standard deviation. (C) Bump−hole pair optimization for GalNAc-T2. Glycosylation by wild-type and double-mutant GalNAc-T2 was compared for UDP-GalNAc (1) and UDP-GalNAc analogs with Peptide-1. Reactions were performed and quantified as in B. Heat map (blue shading) shows percent glycosylated Peptide-1 formed by wild-type or double-mutant GalNAc-T2 with UDP-GalNAc or analogs. Red values represent the mean of technical triplicates.