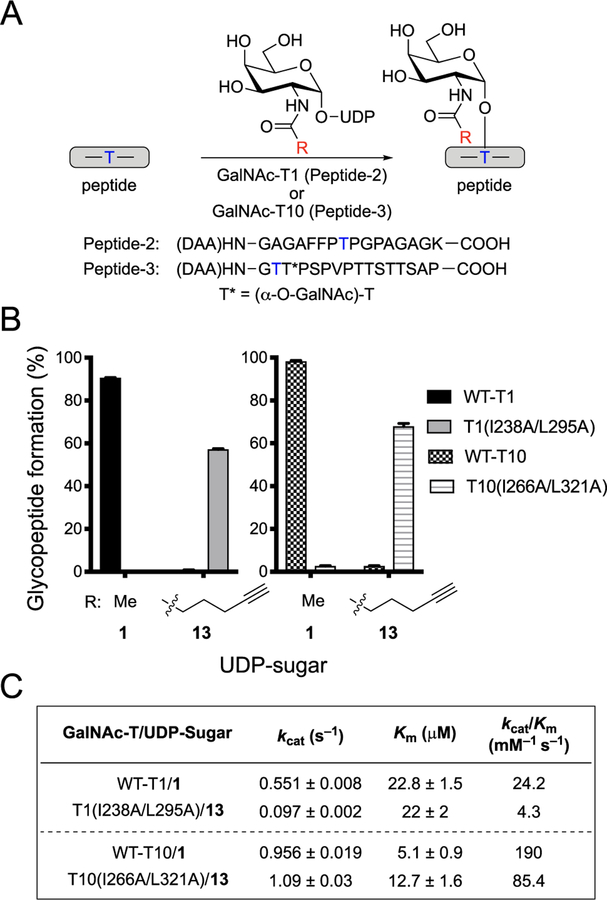
Figure 5.
Orthogonal GalNAc-T and UDP-sugar pairs for GalNAc-T1 and GalNAc-T10. (A) Scheme for glycosylation reaction with GalNAc-T, peptide, and UDP-GalNAc or UDP-GalNAc analog to form glycosylated peptide. Glycosylation reactions with GalNAc-T1 utilized Peptide-2, and reactions with GalNAc-T10 utilized Peptide-3. Blue T indicates the Thr glycosylation site used by the GalNAc-T of interest. (B) Glycopeptide formation by wild-type or double-mutant GalNAc-T1 or GalNAc-T10 with UDP-GalNAc (1) or 13. Reactions were performed as in A. GalNAc-T, UDP-sugar, and peptide were incubated at 37 °C for 1 h (-T10) or 2 h (-T1), and reaction was quenched with aqueous EDTA (150 mM, pH = 8.0). All data represent the mean of technical triplicates, and error bars represent the standard deviation. (C) Kinetic parameters of wild-type and orthogonal GalNAc-T and UDP-sugar pairs. To determine Km and kcat values for UDP-GalNAc and UDP-GalNAc analogs, initial rates were measured by incubating wild-type or double-mutant GalNAc-Ts with varying concentrations of UDP-sugars and a constant concentration of acceptor peptide. For GalNAc-T1, the concentration of UDP-sugars varied from 15.6 to 500 μM, and the concentration of acceptor Peptide-2 was held at 250 μM. For GalNAc-T10, the concentration of UDP-sugars varied from 15.6 to 250 μM, and the concentration of acceptor Peptide-3 was held at 266 μM. Glycosylation was conducted at 37 °C, and three aliquots were taken within 15 min and quenched by addition of aqueous EDTA (150 mM, pH = 8.0). Products were quantified by HPLC separation and peak integration. Enzymatic kinetic parameters were obtained by nonlinear regression fitting using GraphPad Prism. All data represent the mean of technical triplicates, and error depicts the standard deviation.