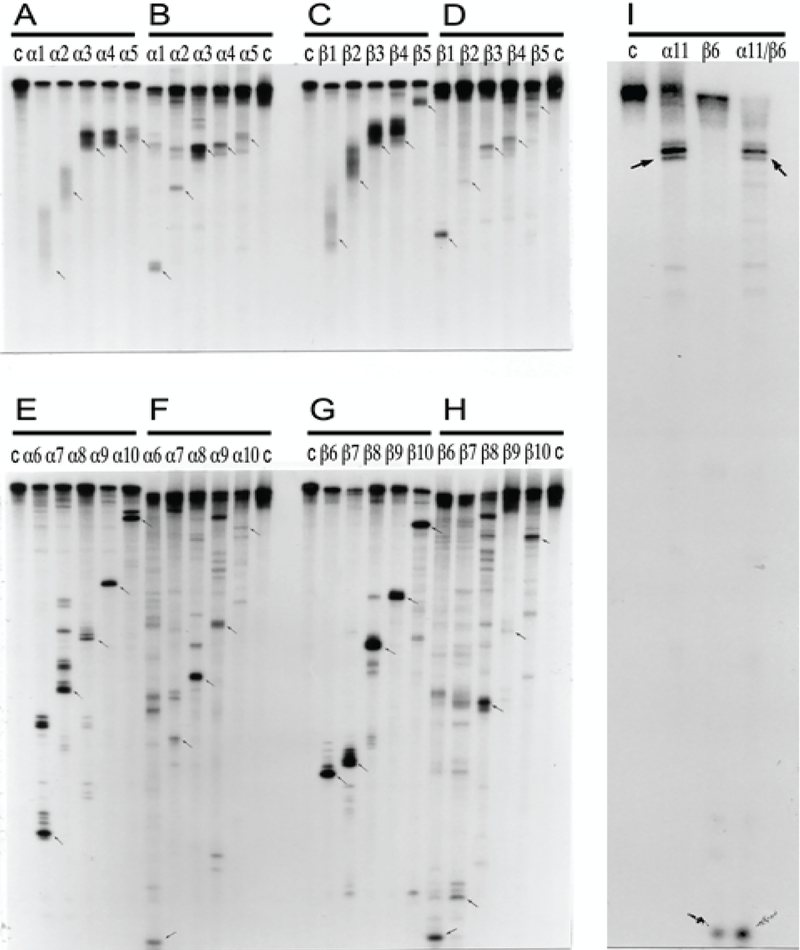
Figure 5: Comparative RNase H mapping analysis of pepRNA (putative end product of mRNA amplification) and conventional globin mRNA.
PepRNA was eluted from methylmercury hydroxide/agarose gels and depleted of regular globin RNA by high stringency hybridization with immobilized globin-specific probes. Conventional globin mRNA, isolated from reticulocytes or eluted from the same gel as pepRNA, was also purified by high stringency hybridization with immobilized globin-specific probes. Purified RNA was labeled at either 5’ or 3’ terminus. RNase H digest was performed as described in Methods section and mapping analysis was carried out by electrophoresis on 8% polyacrylamide-urea gels. Panels A, C, E, G: Regular globin mRNA. Panels B, D, F, H, I: PepRNA. Panels A-D: 3’ labeled RNA. Panels E-I: 5’ labeled RNA. Lanes α1-α11: Alpha-globin-specific oligonucleotides used in RNase H digest assays. Lanes β1- β10: Beta-globin-specific oligonucleotides used in RNase H digest assays. Lane α11/β6: Oligonucleotides α11 and β6 were used jointly in RNase H digest reaction. Sequences and positions of oligonucleotide probes used in digest assays are specified in Methods section. Lane “c”: Control, no oligonucleotide added.