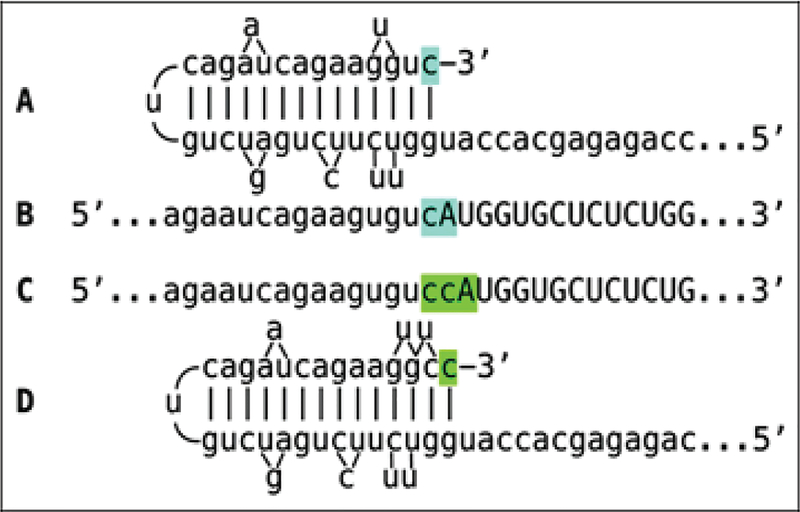
Figure 8: RNA-dependent RNA polymerase can transcribe the cap “G” of mRNA.
Data shown are adapted from Figure 2, top panel. Uppercase letters-nucleotide sequence of the sense strand; lowercase letters-nucleotide sequence of the antisense strand. “c” highlighted in blue-3’-terminal nucleotide of the antisense strand corresponding to the transcription start site of mRNA; “cA” highlighted in blue-the projected junction structure in the absence of the cap “G” transcription. “c” highlighted in green-transcript of the cap “G”; “ccA” highlighted in green-the resulting junction structure when cap “G” is transcribed. A: Projected self-priming configuration of the antisense strand in the absence of the cap “G” transcription. B: Projected nucleotide sequence of the sense/antisense junction in the absence of the cap “G” transcription. C: Detected nucleotide sequence of the sense/antisense junction. D: Self-priming configuration of the antisense strand as defined by experimental results. Note that the genomic sequence upstream of the TSS cannot account for the additional 3’-terminal “C” in the antisense strand.