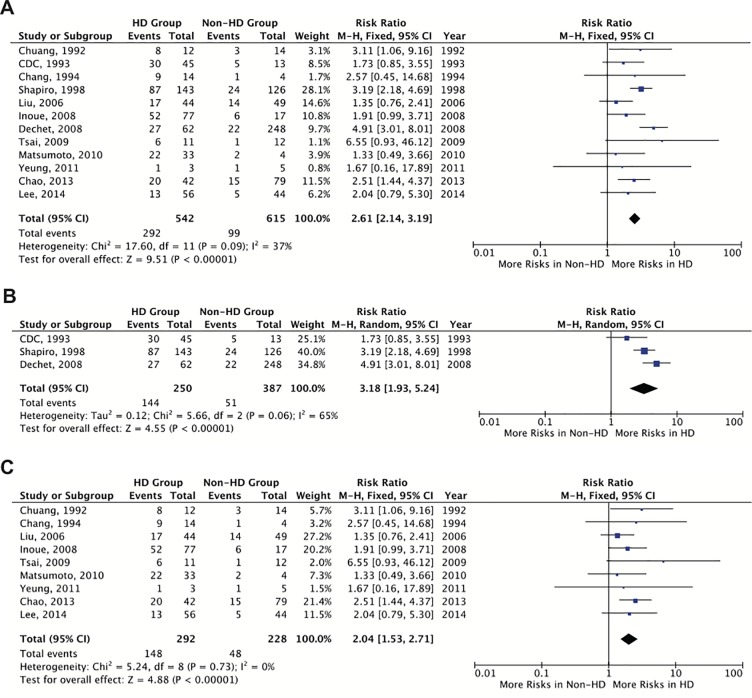
Fig 2.
Risk of mortality of Vibrio vulnificus necrotizing skin and soft tissue infections in patients with hepatic disease compared to those without it: (A) the world’s coastal areas; (B) the western Atlantic coastal areas; and (C) the western Pacific coastal areas. “Study or subgroup” on the Y-axis refers to first author and publication year. “Events” refers to the number of patients who died. “Total” refers to the number of patients in that group. “Weight” refers to the influence of each study on overall estimate (weights are from fixed effect analyses for I2 < 40% and random effect analyses for I2 ≥ 40%). For each study the central square indicates risk ratio, the line represents the 95% confidence interval (CI), and the size of the square reflects the study’s weight in the pooling. “Overall estimate” refers to pooled estimate of risk ratio after mathematical combination of all studies. The X-axis indicates the scale and the direction of the effect of hepatic disease on the risk of mortality. I-squared denotes the extent of heterogeneity in study outcomes, with a hypothetical value of 100% meaning considerable heterogeneity and 0% meaning no heterogeneity between studies.