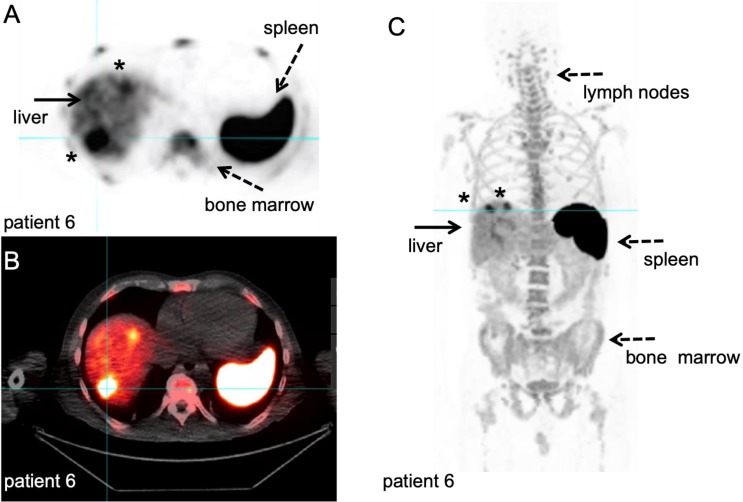
Figure 8.
89Zr-labelled anti-CD8 minibody PET/CT. Patient with newly diagnosed Hepatocellular Carcinoma on immunotherapy for 12 weeks prior to IV injection of 111 MBq of 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C. PET/CT images were acquired 24 hours after injection, for information on the molecule we refer to the publications that are currently in preparation. A-B: Axial 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C PET and corresponding axial fused PET/CT images demonstrate two focal areas of 89Zr-Df- IAB22M2C uptake in the liver (filled arrow). The 89Zr-Df- IAB22M2C uptake in the lateral aspect of the right hepatic lobe corresponds to a 2.5 cm lesion (asterisk). The 89Zr-Df- IAB22M2C uptake in the anterior aspect of the left hepatic lobe (asterisk) is due to co-localization of 89Zr-Df- IAB22M2C to an occult hepatic metastasis. C: The coronal MIP PET image shows the intense uptake of 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C in reference tissues with known areas of high CD8 TIL cells such as the lymph node (LN), spleen and bone marrow (dashed arrows). The two foci of 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C focal uptake within the liver (filled arrow) is also clearly seen on this projection due to the relatively low hepatic background activity compared to CD8 rich tissues. This case demonstrates the value of 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C PET scans to detect CD8 T-cells in the tumour microenvironment. With courtesy of ImaginAb Inc.