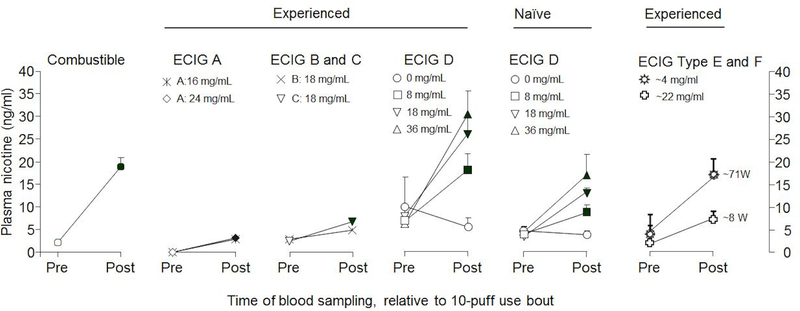
Figure 2. Variability in e-cigarette nicotine delivery (adapted from Breland et al. [3]).
Mean (SEM) plasma nicotine concentration from different human laboratory studies and different products with blood sampled before and immediately after a 10-puff product use bout. Combustible cigarette data from [59]. ECIG A is a first generation device [61]. ECIG B is a first generation device, and ECIG C is a third generation device [63]. ECIG D is a second generation device [70,71]. Data for ECIG Type E are from a group of second generation devices (mean power output = ~8 W), and data for ECIG Type F are from a group of third generation devices (mean power output = ~71 W) [35]; note that the higher-powered ECIG Type F delivers more nicotine to the user despite being paired with a lower concentration nicotine liquid (i.e., ~4 mg/ml) [69]. Figure adapted from Breland et al., 2017 [3]. Copyright 2016 New York Academy of Sciences.