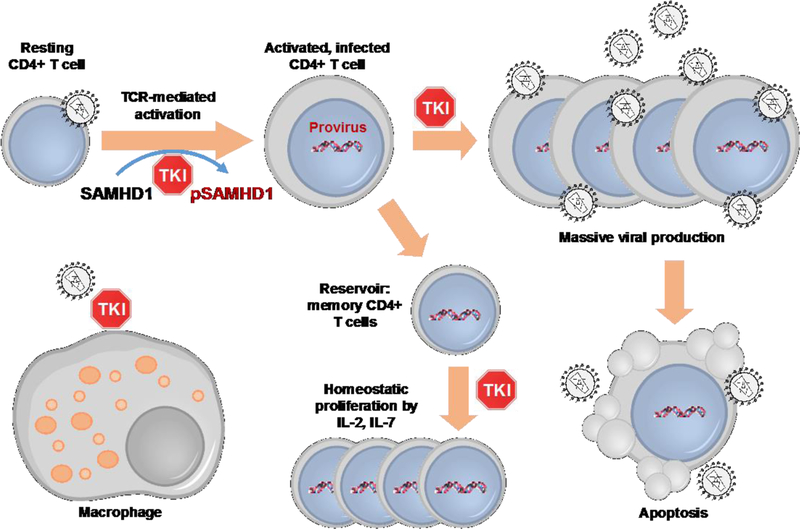
Figure 1.
Different mechanisms by which TKIs are thought to interfere with HIV-1 reservoir formation and replenishment. TKIs such as dasatinib may interfere with HIV-1 reservoir at several levels: a) blocking SAMHD1 phosphorylation to preserve its antiviral activity and avoid the infection of new target cells; b) impeding the proliferation of clonally expanded, infected CD4+ T cells during activation of the immune response; c) interfering with the γC-cytokine-induced homeostatic proliferation of infected memory CD4+ T cells that contribute to the continuous expansion and maintenance of the latent reservoir; d) impeding the infection of long-lived cells such as macrophages that may reside in tissues with limited access to drug exposure such as CNS.