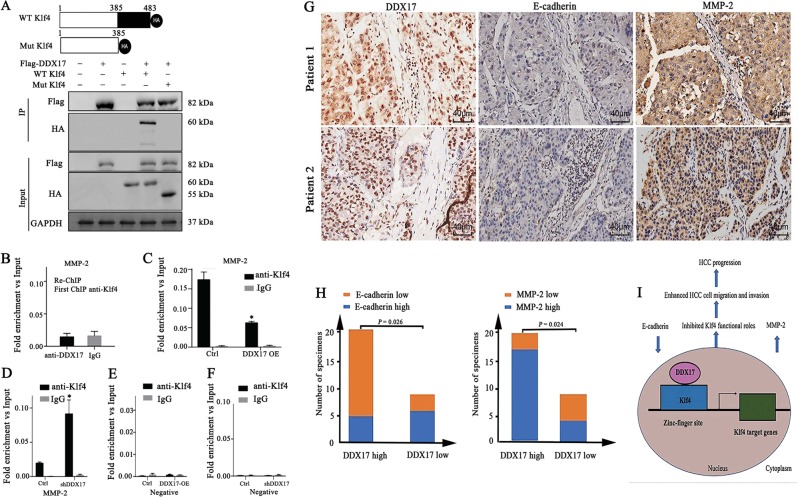
Fig. 6. DDX17 regulates the expression of MMP-2 by inducing dissociation of Klf4 on chromatin and its expression is significantly correlated with E-cadherin and MMP-2 expressions in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues.
a Brief description for wild type and mutant type of Klf4 and interaction between wild type/mutant type Klf4 and DDX17 was assessed using CO-IP in HEK293T cells. b Re-ChIP assay showed no binding between DDX17 and Klf4 at MMP-2 promoter. c, d The intensity of Klf4 binding on MMP-2 promoter was detected in DDX17 overexpression and knockdown was detected by ChIP-qPCR. e, f The intensity of Klf4 binding on negative promoter was detected by ChIP-qPCR after overexpression and knockdown of DDX17. g Representative images of immunohistochemical staining of DDX17, E-cadherin, and MMP-3 in tumor tissues. h Spearman’s correlation analysis of DDX17 and E-cadherin expression, DDX17 and MMP-2 expression. i Model: Diagrammatical representation, elucidating DDX17-mediated suppression of Klf4 transcriptional activity in hepatocellular carcinoma. DDX17 binds to zinc-finger domain of Klf4, subsequently inhibits Klf4 target genes including E-cadherin and MMP-2. Decreased E-cadherin expression and increased MMP-2 expression result in potentiating HCC cell migration and invasion, thus conductive to HCC progression. *p < 0.05