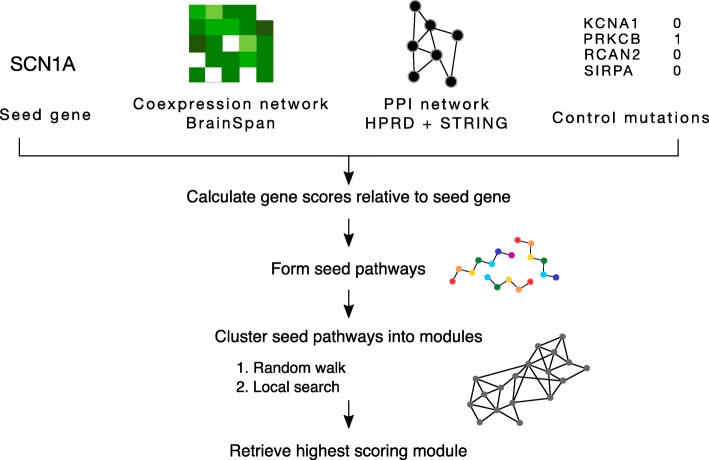
Fig. 1.
General overview of MAGI-S. A seed gene (e.g., SCN1A), protein-protein interaction (PPI) network, co-expression network, and LOF mutations in control samples are provided to MAGI-S to produce a seed centric module. Each gene in the PPI and co-expression networks is assigned a score based on the gene’s degree of co-expression with the seed gene relative to all other genes in the networks. Seed pathways are high-scoring simple paths formed from genes that are highly co-expressed relative to the seed gene, connected in the PPI network, and have a low number of LOF variants in control samples. Seed pathways are clustered into modules via a random walk of a graph created by seed pathways, and the total score of a module is improved by local search (similar to the MAGI algorithm in Hormozdiari et al. [16]). MAGI-S is run with varied parameters related to module size, minimum co-expression, and minimum PPI density, and the highest scoring module is retrieved. We have used the human developmental data from BrainSpan Atlas for the co-expression network construction. Furthermore, the combination of protein interactions from HPRD and STRING datasets was used as the PPI networks in our analysis