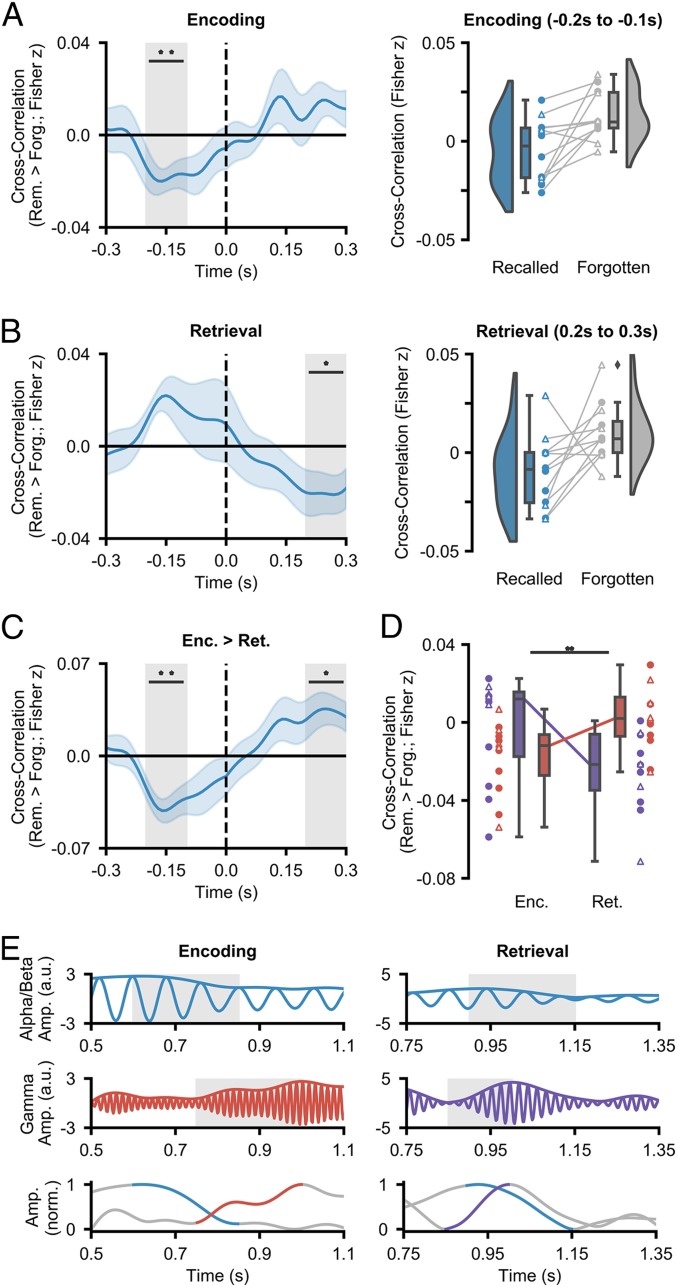
Fig. 4.
Hippocampal–neocortical time-series cross-correlations. (A) Mean cross-correlation (with shaded SEM; Left) between the hippocampal fast gamma power and ATL alpha/beta power during encoding (**Pfdr < 0.01). ATL power decreases precede hippocampal fast gamma power increases. Raincloud plot (Right) depicts the difference in cross-correlation between remembered and forgotten items. Colored circles represent participants who took part in experiment 1. Uncolored triangles represent participants who took part in experiment 2. (B) Mean cross-correlation (with shaded SEM; Left) between the hippocampal slow gamma power and ATL alpha/beta power during retrieval (*Pfdr < 0.05). Hippocampal slow gamma power increases precede ATL alpha/beta power decreases. Raincloud plot (Right) depicts the difference in cross-correlation between remembered and forgotten items. Colored circles represent participants who took part in experiment 1. Uncolored triangles represent participants who took part in experiment 2. (C) The contrast of cross-correlation activity between encoding and retrieval (*Pfdr < 0.05, **Pfdr < 0.01). (D) Mean cross-correlation between neocortical alpha/beta power and hippocampal gamma power (slow in purple; fast in red; with SEM) as a function of memory operation (Top, subject-level; Bottom, electrode pair-level). A repeated-measures ANOVA reveals an interaction between hippocampal gamma frequency and memory task when predicting memory-related hippocampal–neocortical cross-correlation (**P < 0.01). (E) Filtered single-trial traces at encoding (Left) and retrieval (Right) in the ATL (Top) and hippocampus (Middle). The envelopes of these traces are plotted (Bottom). During encoding, a reduction in ATL alpha/beta activity precedes an increase in hippocampal fast gamma power. During retrieval, an increase in hippocampal slow gamma power precedes a decrease in ATL alpha/beta activity.