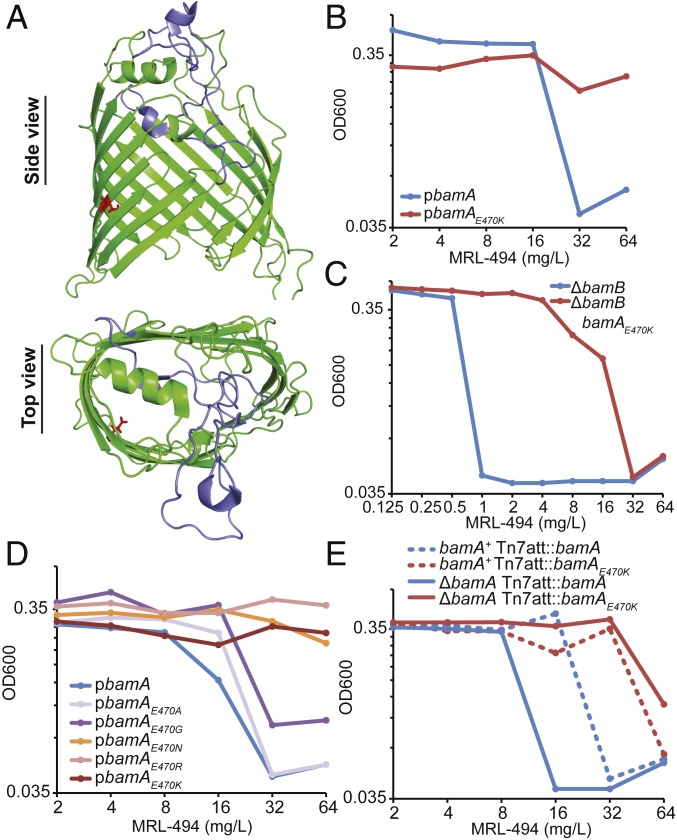
Fig. 2.
BamAE470K provides resistance to MRL-494 and restores OMP biogenesis. (A) A structure of BamA β-barrel domain (59) is shown a side view (from the plane of the OM) and a top view (from outside the OM). The E470 is indicated as red sticks, while extracellular loop 6 is indicated in blue. (B) Expression of bamAE470K results in increased resistance to MRL-494. BamA-depletion strains carrying the indicated plasmids were grown without arabinose to deplete BamA from the chromosomal copy of bamA, and MRL-494 resistance was then assayed by the MIC procedure. OD600 following overnight MRL-494 treatment is shown. Data are representative of 3 biological replicates. (C) Expression of bamAE470K results in a large increase in MRL-494 resistance in a ΔbamB background. ΔbamA ΔbamB with either wild-type bamA or bamAE470K at the Tn7 attachment site were assayed for MRL-494 resistance by the MIC procedure. OD600 following overnight MRL-494 treatment is shown. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. (D) Resistance to MRL-494 correlates with the residue at BamAE470. Cells carrying plasmids with various alleles at bamAE470 were treated as in B and assayed for MRL-494 resistance. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments. (E) Expression of bamA in merodiploid increases resistance to MRL-494. Strains expressing bamA or bamAE470K in merodiploid or haploid were assayed for MRL-494 susceptibility through the MIC procedure. OD600 following overnight MRL-494 treatment is shown. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments.