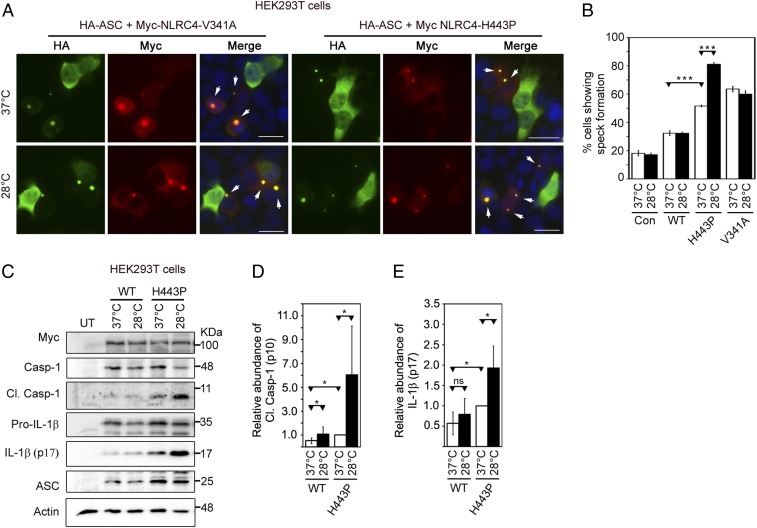
Fig. 5.
NLRC4-H443P–expressing cells exposed to subnormal temperature show an increase in inflammasome formation and caspase-1 activation. (A) Representative immunofluorescence images show the effect of exposure to subnormal temperature on ASC-speck formation in cells expressing HA-ASC along with NLRC4-V341A or NLRC4-H443P. One set of cells was shifted to 28 °C for 6 h after 12 h of transfection, while the other set remained at 37 °C. White arrows indicate specks. DAPI was used to stain the nucleus. (Scale bars, 20 μm.) (B) Quantitation of ASC-speck formation in response to subnormal temperature (n = 6). ***P < 0.0005. Con, control. (C) Western blot analysis of lysates of HEK293T cells expressing caspase-1 (Casp-1) and HA-ASC along with Myc-NLRC4, Myc-NLRC4-H443P, or Myc-NLRC4-V341A. One set of cells was exposed to 28 °C for 6 h after 18 h of expression, while the other set remained at 37 °C. Lysates were analyzed for the presence of cleaved (Cl.) Casp-1 (p10). UT, untransfected. The bar diagrams show quantitation of the effect of exposure to subnormal temperature on the relative abundance of Cl. Casp-1 normalized with caspase-1 p45 signal (D) and IL-1β normalized with pro–IL-1β signal (E) (n = 6). *P < 0.05. ns, not significant.