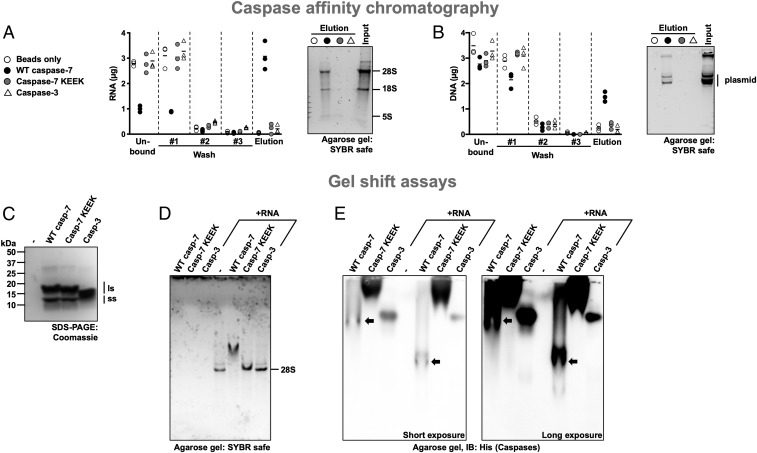
Fig. 4.
Caspase-7’s exosite binds nucleic acids. (A and B) Binding of RNA and DNA to caspase affinity columns. Purified His-tagged caspases were immobilized on 0.2 mL IMAC resin and incubated with 7.2 µg total RNA in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (A) or plasmid DNA (B), washed 3 times with PBS, and eluted using 1.25 M NaCl in PBS. Then nucleic acids were quantified at 260 nm, separated on a 1% agarose gel, and stained using SYBR Safe. WT caspase-7 retains nucleic acid more than the exosite mutant or caspase-3. (C) Coomassie gel stain of the caspases used in this figure showing the large (ls) and small (ss) subunits of the peptidase. (D and E) Caspase-7 forms a complex with RNA. Caspases alone or combined with RNA were analyzed on a nondenaturing agarose gel to assess alteration in RNA migration due to the interaction with a caspase (D). The agarose gel used in D was transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane and analyzed by immunoblotting using an anti-His tag antibody (E). RNA alters the gel mobility of WT caspase-7 but not that of the exosite mutant or caspase-3. Short and long exposures of the membrane are shown; in E, black arrows point to bands containing WT caspase-7.