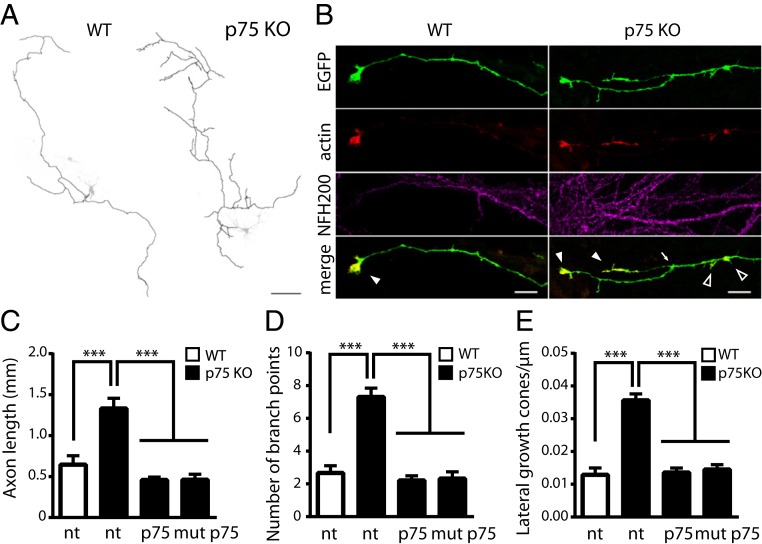
Fig. 6.
wt p75NTR and mut p75NTR mediate growth cone collapse and regulate axon complexity. (A) Hippocampal neurons from wt (Left) and p75NTR KO (Right) mice. Axons from EGFP- and TagRFP-actin–expressing neurons are drawn in black and superimposed to the EGFP channel (grayscale). (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (B) Magnification of axon terminals from images in A also showing immunofluorescence for the axonal marker NF-200. TagRFP-actin accumulates at growth cones. Branching points (arrow), terminal growth cones (filled arrowheads), and lateral growth cones (empty arrowheads) are indicated. (Scale bars, 5 μm.) Quantification of axon length (C), number of branch points (D), and number of lateral growth cones per length unit (E) are illustrated in nontransfected (nt) wt hippocampal neurons (white columns), in nt p75NTR KO hippocampal neurons (black columns), or transfected with wt p75NTR or mut p75NTR constructs (wt/mut p75NTR, black columns). ***P < 0.001, Kruskal–Wallis test (Dunn’s multiple comparisons). Bars are mean ± SEM.