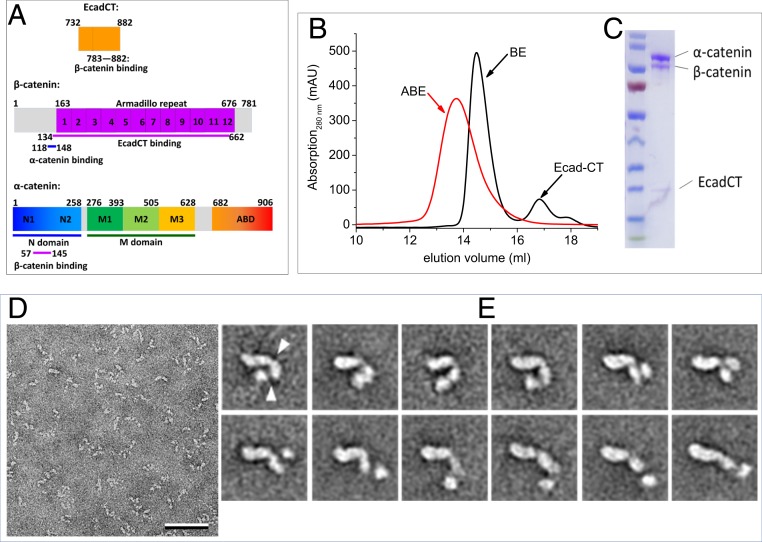
Fig. 1.
Conformational variability of the ABE complex revealed by negative stain EM. (A) Amino acid sequence and domain boundaries of EcadCT, α-catenin, and β-catenin. Previous studies showed that residues 783 to 882 in EcadCT bind to the armadillo repeat domain of β-catenin at residues 134 to 662 (23) and that residues 57 to 145 in the N domain of α-catenin bind to β-catenin at residues 118 to 148 (24). (B and C) Gel filtration profile (B) and sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel of the reconstituted ABE complex (C). (D) Electron micrograph area of negatively stained ABE complex. (Scale bar: 50 nm.) (E) Selected class averages of negatively stained ABE complex obtained with the ISAC procedure (SI Appendix, Fig. S1 shows all averages). Particles are shown from a more compact conformation starting in the upper left to a more extended conformation in the lower right. The arrowheads in the first average indicate the apparent hinge points around which the domains can move. Side length of individual averages: 31.2 nm.