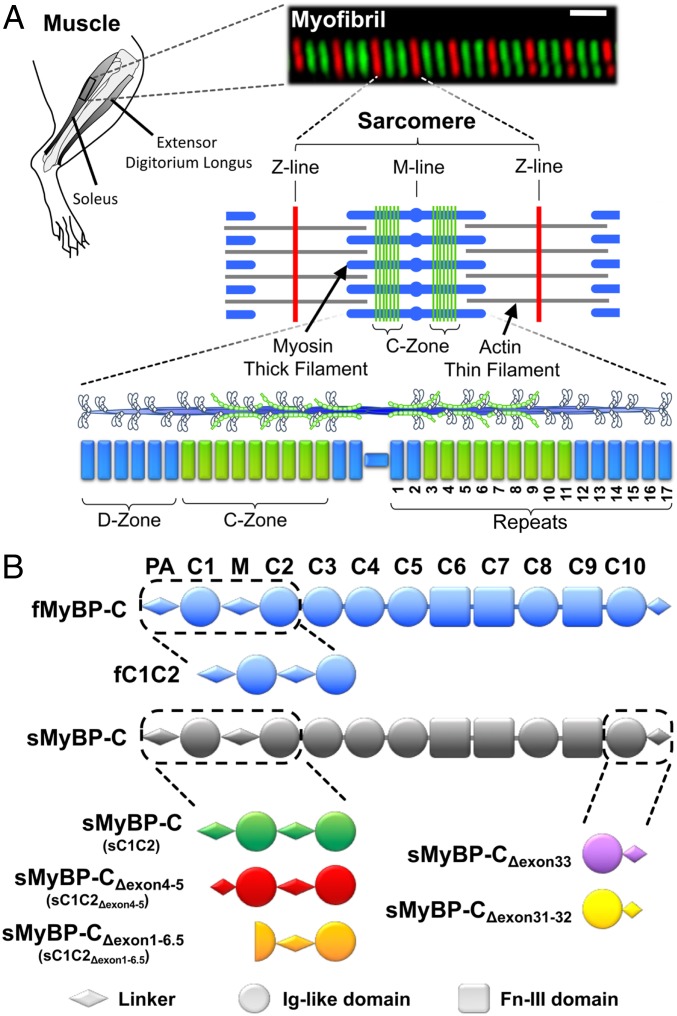
Fig. 1.
MyBP-C isoforms and their localization in rat skeletal muscle. (A) In this study, contractile protein preparations were obtained from the rat hind limb soleus and extensor digitorum longus. An immunofluorescent image of a soleus myofibril composed of 8 sarcomeres, whose boundaries are identified by antibodies to the Z-line protein, α-actinin (red). Antibodies against slow-type MyBP-C (green) highlight the distinct regions (C-Zones) in the sarcomere center where MyBP-C is localized. The sarcomere is comprised of myosin thick filaments (blue) and actin thin filaments (gray). Striated muscle myosin forms bipolar thick filaments where each half thick filament consists of 17 repeats that demarcate the 43-nm myosin head helical repeat. MyBP-C within the C-Zone occupies ∼9 repeats near the thick filament center where the ends of the thick filament are devoid of MyBP-C (D-Zone). (B) Skeletal MyBP-C consists of 7 Ig-like (Ig-like, circles) and 3 fibronectin-III (Fn-III, rectangles) domains named C1 through C10. A proline-alanine rich domain (PA) precedes the C1 domain and an M-domain linker (M) exists between the C1 and C2 domains. In skeletal muscle,1 fast-type MyBP-C and multiple slow-type MyBP-C splice isoforms are present. Slow-type MyBP-C is alternatively spliced at its N and C terminus. See SI Appendix, Figs. S1 and S2 for isoform-specific sequences.