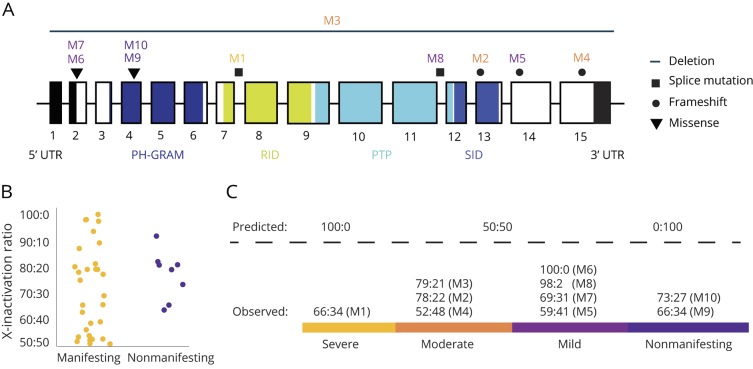
Figure 2. MTM1 gene mutation locations and X-inactivation ratios for manifesting and nonmanifesting carriers.
(A) Gene structure and location of mutations in the MTM1 gene. Exons are represented as boxes. Mutation locations are indicated with mutation type coded by shape. The myotubularin protein contains 4 domains: the pleckstrin homology glucosyltransferases, Rab-like GTPase activators and myotubularins (PH-GRAM) domain, Rac1-Induced recruitment domain (RID), protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) and SET-interacting domain (SID). (B) X-inactivation ratios for MTM1-related myopathy manifesting and nonmanifesting carriers reported in the literature show a range of ratios without a clear pattern. (C) X-inactivation patterns are expected to follow predicted ratios if X-inactivation is the primary driver of symptom expression and severity; however, the prediction does not hold up in our cohort, suggesting the X-inactivation model of disease expression is incomplete, and additional factors exist.