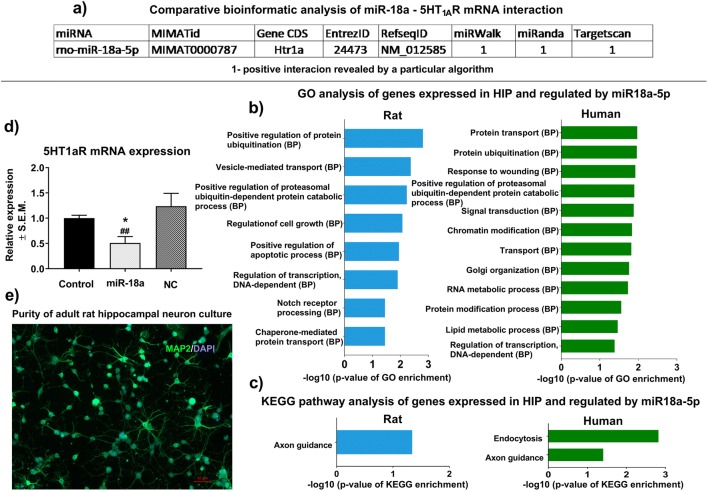
Fig. 2.
a Comparative bioinformatic analysis with the use of miRWalk 2.0 software shows that miR-18a-5p is a potential posttranscriptional regulator of mRNA encoding 5-HT1AR. 1—indicates positive predicted interaction between miR-18a-5p and mRNA encoding 5-HT1AR as revealed by a particular algorithm. b Gene enrichment analysis revealed that genes potentially regulated by miR-18a-5p and expressed in HIP are significantly involved in different biological processes associated with normal brain functioning in rats (left panel) and humans (green panel). All biological processes were calculated by hypergeometric distribution followed by p value correction for multiple testing. c KEGG pathway analysis of genes expressed in HIP and regulated by miR-18a-5p revealed that this miR is involved in the regulation of axonogenesis in both humans (right panel) and rats (left panel) and endocytosis in humans (right panel). KEGG pathways were by hypergeometric distribution followed by p value correction for multiple testing. d In vitro validation of the regulatory role of miR-18a-5p on the expression level of mRNA encoding 5-HT1AR. RT-PCR analysis shows that neurons transfected with 20 nM of miR-18a-5p expressed significantly lower levels of 5-HT1AR mRNA compared to non-transfected as well as neurons stimulated with negative control siRNA (n = 4–5),*p < 0.05 vs. control, ##p < 0.01 vs. negative control. e Immunocytochemical examination of the purity of the adult hippocampal neuronal cell culture. Double-staining for MAP2 and GFAP markers revealed that a vast majority of cultured cells were MAP2-positive neurons (green cells). There were no recorded GFAP-positive (orange cells) astroglial cells in the culture