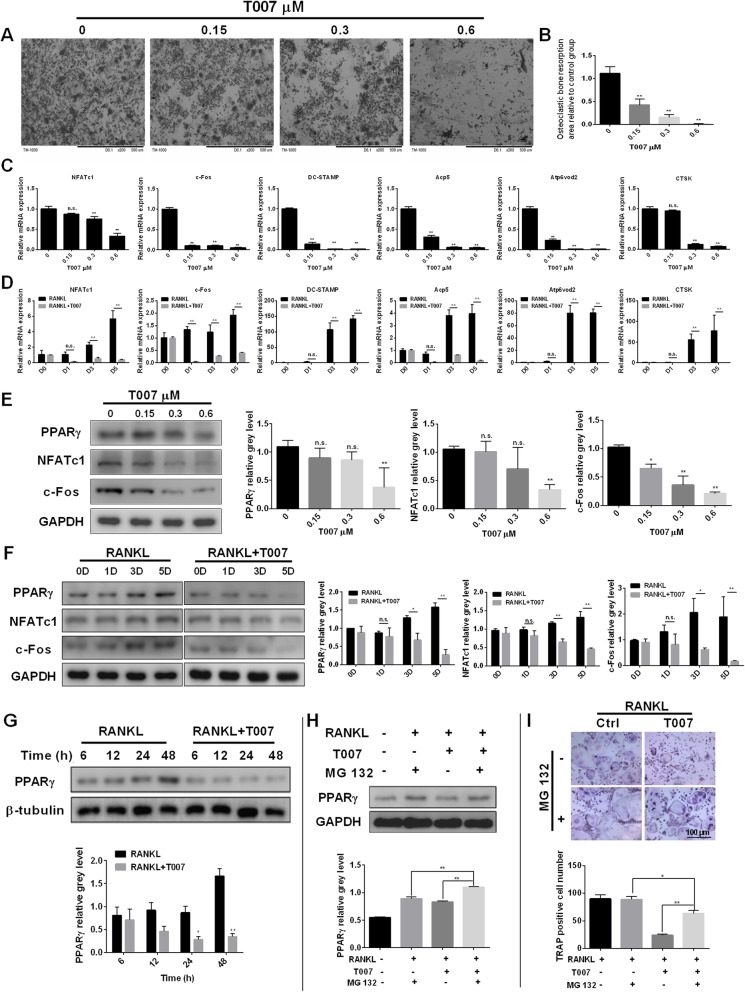
Fig. 2.
T007 inhibited osteoclastic bone resorption and RANKL-induced osteoclast-specific gene expression in vitro. a BMMs were seeded onto bone slices and treated the same as described in Fig. 1d for 7 days and scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of bone resorption pits are shown. b Resorption pit area measurements by using Image J. c NFATc1, c-Fos, DC-STAMP, Acp5, Atp6v0d2, and CTSK expression in BMMs treated with the indicated T007 concentrations for 5 days. d NFATc1, c-Fos, DC-STAMP, Acp5, Atp6v0d2, and CTSK expression in BMMs treated with T007 (0.6 μM) for 0, 1, 3 or 5 days. e BMMs were treated with various concentrations of T007. Cell lysates were analyzed using western blotting. The expression of PPARγ, NFATc1, and c-Fos was evaluated. f, g BMMs were treated with RANKL, with or without 0.6 μM T007 for the indicated periods. Cell lysates were analyzed using western blotting. The expression of PPARγ, NFATc1, and c-Fos was evaluated. h The effect of T007 on the expression of PPARγ in BMMs was rescued treated with 1 μM of MG 132. i The number of TRAP-positive BMMs after treatment with RANKL, T007 (0.6 μM), and MG 132 (1 μM) for 7 days. All experiments were performed at least three times. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 compared with the control group