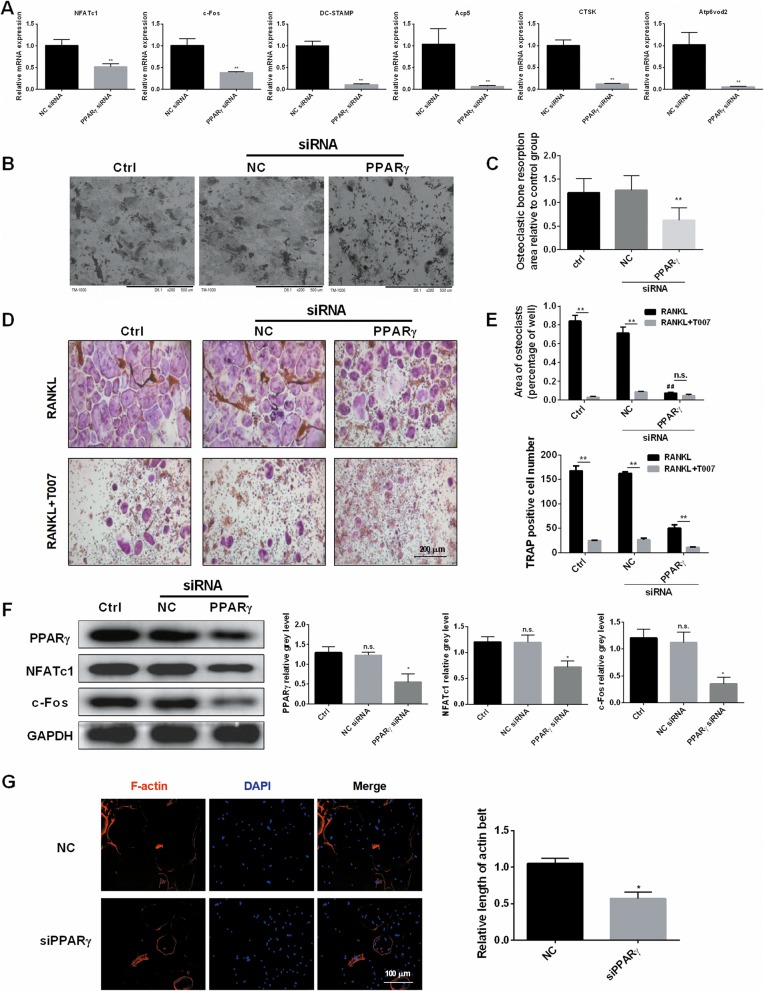
Fig. 3.
Loss of function by knocking down PPARγ impaired RANKL-induced osteoclast-specific gene expression and inhibited osteoclast differentiation in vitro. a Expression of the osteoclast-specific genes NFATc1, c-Fos, DC-STAMP, Acp5, Atp6v0d2, CTSK in RAW264.7 cells following the transfection with PPARγ siRNA. Negative siRNA was used as a control. b, c The bone resorption pits of BMMs after the transfection with siRNA were detected using scanning electron microscope (SEM) images, and the resorption pit area measurements by using Image J. Untreated cells were used as a control. d, e The number and area of TRAP-positive BMMs after the transfection with siRNA and the treatment with T007 (0.6 μM). Untreated cells were used as a control. f BMMs were transfected with siRNA, untreated cells were used as a control. Cell lysates were analyzed using western blotting. The expression of PPARγ, NFATc1 and c-Fos was evaluated. g The effect of siPPARγ on the formation of F-actin ring. All experiments were performed at least three times. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 compared with the control group. # # P < 0.01 compared with the RANKL group