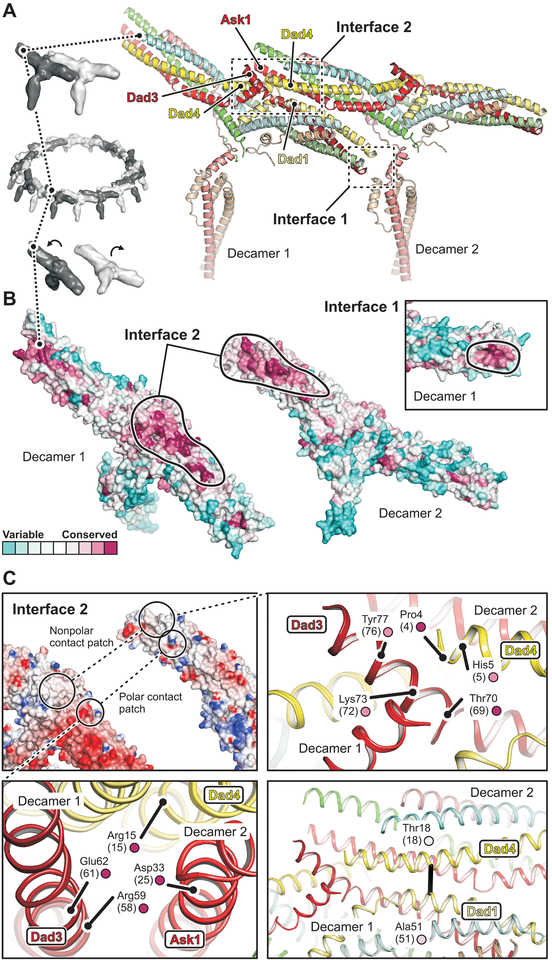
Fig. 2. Structural basis of DASH/Dam1c oligomerization.
(A) Close-up view of two adjacent protomers (labeled decamer 1 and 2) within the DASH/Dam1c ring. Interfaces 1 and 2 are boxed. The subunits are colored as in Fig. 1. (B) Surface residue conservation of DASH/Dam1c in the fungal kingdom. Conservation scores were calculated with ConSurf (46) and mapped onto our structure. The protomers are flipped open, exposing interface 2. Black lines surround the inter-complex binding footprints. The inset shows a close-up view of interface 1 for decamer 1 only. (C) Interface 2 has patches of polar and hydrophobic contacts. Top left, surface representation of the two protomers colored according to the electrostatic potential, calculated with DelPhi (47). Bottom left, close-up view of the polar contact patch. Relevant amino-acids are labeled with residue numbers (S. cerevisiae numbers in parenthesis) and conservation score (small circle, color as in B). Top right, close-up view of the hydrophobic patch. Bottom right, interface molecular contact inferred from DCA of residue coevolution shown as a black line.