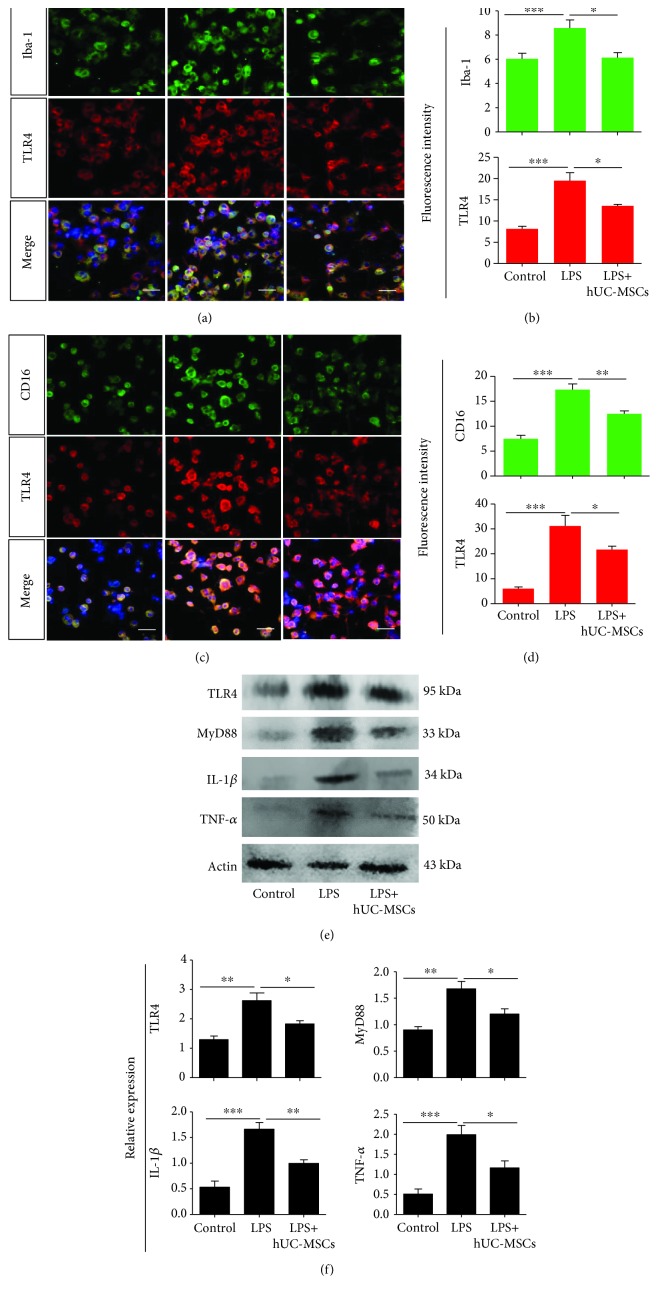
Figure 8.
hUC-MSCs modulate TLR4 pathway-related agents and proinflammatory mediator levels in LPS-treated BV2 cells. (a and b) Double staining for iba-1 (green) and TLR4 (red), showing poor colocalization of iba1 and TLR4. The fluorescence intensity showing reduced expression of iba-1 and TLR4 in LPS-treated BV2 cells after hUC-MSC treatment (n = 4/group; ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared with one-way ANOVA with Turkey's post hoc tests). (c and d) Double staining for CD16 (green) and TLR4 (red) showing colocalization of CD16 and TLR4. The fluorescence intensity showing reduced expression of CD16 and TLR4 in LPS-treated BV2 cells after hUC-MSC treatment (n = 4/group; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared with one-way ANOVA with Turkey's post hoc tests). (e and f) Quantification of TLR4, MyD88, IL-1β, and TNF-α expression by western blot analysis showing a significant decrease in TLR4, MyD88, IL-1β, and TNF-α expression after hUC-MSC treatment (n = 4/group; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared with one-way ANOVA with Turkey's post hoc tests). Scale bar: 50 μm.