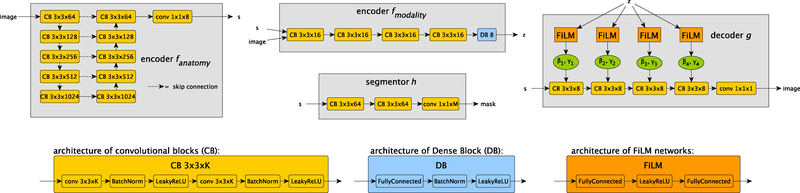
Fig. 2:
The architectures of the four networks that make up SDNet. The anatomy encoder is a standard U-Net (Ronneberger et al., 2015) that produces a spatial anatomical representation s. The modality encoder is a convolutional network (except for a fully connected final layer) that produces the modality representation z. The segmentor is a small fully convolutional network that produces the final segmentation prediction of a multi-class mask (with L classes) given s. Finally the decoder produces a reconstruction of the input image from s with its output modulated by z through FiLM normalisation (Perez et al., 2018). The bottom of the figure details the components used throughout the four networks. The anatomical factor’s channels parameter C, the modality factor’s size nz, and the number of segmentation classes L depend on the specific task and are detailed in the main text.