Figure 4.
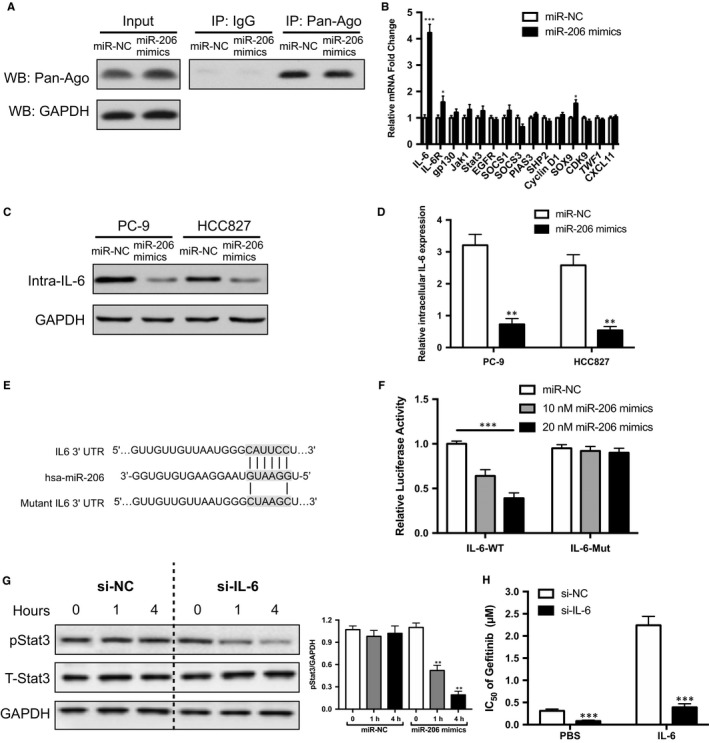
Intracellular IL‐6 was the direct target of miR‐206. A, Western blot was used to detect the Ago2‐RISC complex using the Ago antibody in PC‐9 cells with miR‐206 mimics or control; IgG was used as a negative control. B, RNA‐ChIP analysis was conducted to detect levels of mRNAs that bound with the Ago2‐RISC complex from PC‐9 cells transfecting with miR‐206 mimics or control for 4 h, as measured by qRT‐PCR; C, Western blot or D, qRT‐PCR was used to detect the protein or mRNA levels of intracellular IL‐6 in PC‐9 and HCC827 cells; PC‐9 and HCC827 cells were cultured for 72 h with 10 ng/mL rhIL‐6 prior to miR‐206 mimics or control treatment, and the cells collected for WB were washed five times to remove remnant membrane‐bounded rhIL‐6 with PBS before lysis. E, bioinformatics predicted and mutated miR‐206 binding sites with IL‐6. F, luciferase activity of the reporter construct containing the wild‐type or mutant 3' UTR of IL‐6 was measured after cotransfection with different amounts of miR‐206 mimics in PC9 cells. G, knockdown of intracellular IL‐6 abolished IL‐6‐induced p‐Stat3 in PC‐9 cell; PC‐9 cells were cultured for 72 h with 10 ng/mL rhIL‐6 prior to siRNA transfection. H, knockdown of intracellular IL‐6 decreased gefitinib resistance in PC‐9 cells. The mean ± SD values are shown. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001
