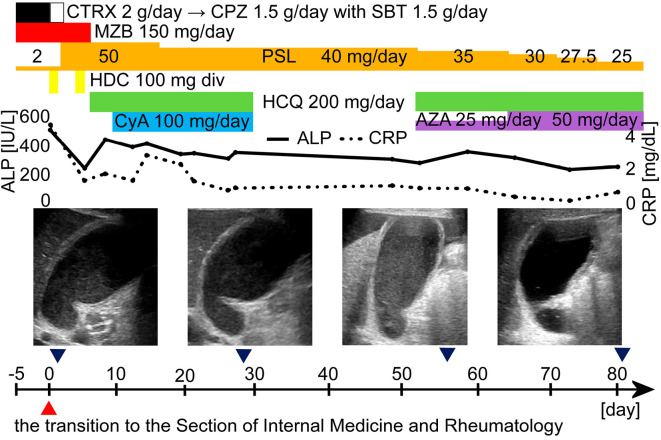
Figure 3.
The clinical course of the patient, a 69-year-old Japanese woman. Abdominal ultrasonography showed the thickening of the gallbladder wall and the swelling and tension of the gallbladder. Because SLE-associated AAC was suspected, antibiotics were stopped, and the PSL dose was increased to 50 mg/day. HCQ 200 mg/day and CyA 100 mg/day were added, and the patient’s general condition improved. After that, however, uroseptic shock occurred, and PSL alone was continued. After the septic shock was controlled, HCQ was started again, and the CyA was switched to AZA 25 mg/day. After the therapy, her general condition became good again, and the ALP and CRP values improved. The AZA dose was increased to 50 mg/day, and the PSL dose was reduced to 25 mg/day. After the introduction of azathioprine, the swelling and tension of the gallbladder also improved. ALP: alkaline phosphatase, AZA: azathioprine, CPZ: cefoperazone, CRP: C-reactive protein, CTRX: ceftriaxone, CyA: cyclosporin A, div: drip intravenous injection, HCQ: hydroxychloroquine, HDC: hydrocortisone, MZB: mizoribine, PSL: prednisolone, SBT: sulbactam