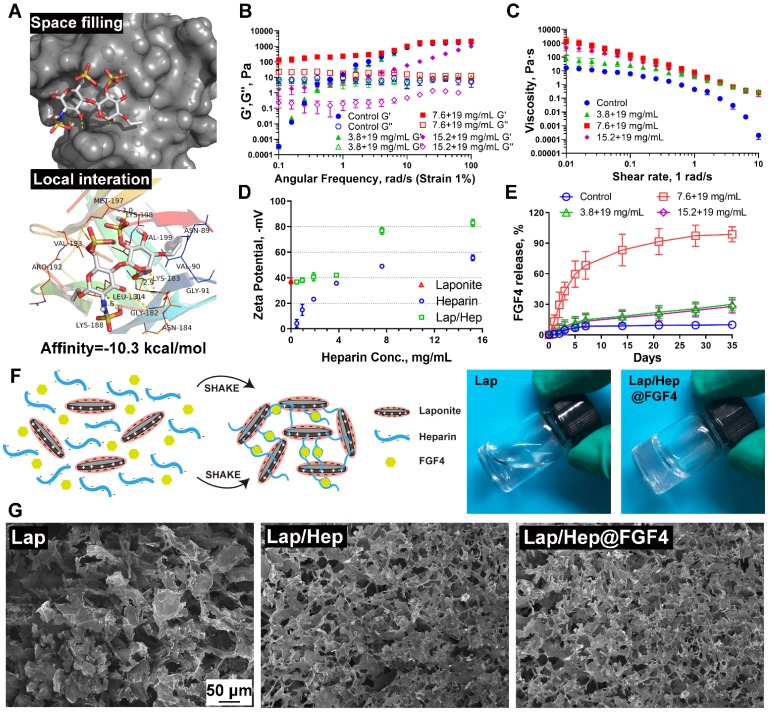
Figure 1.
Characterization of Laponite, Lap/Hep and Lap/Hep@FGF4 hydrogels. (A) Docking studies were performed as described in Materials and methods. The protein residues are shown in a ribbon model. The space filling models show the binding of heparin monomer in the FGF4 binding pockets. (B) Angular frequency sweep measurements of Laponite and Lap/Hep gels. (C) Viscosity change of Laponite and Lap/Hep gels with different concentrations as a function of shear rate. (D) Zeta potential measurements of Laponite, heparin and Lap/Hep as a function of heparin concentration. (E) Cumulative release of FGF4 from Laponite and Lap/Hep gels. (F) Schematic illustration of gelation between heparin-FGF4 complex and Laponite to form Lap/Hep@FGF4 gel. Once the two components are mixed with manually shaking, the whole solution turns into transparent gel. (G) SEM images of the lyophilized Laponite, Lap/Hep and Lap/Hep@FGF4 hydrogels. All experiments were performed in triplicate and data are presented as Mean ± SD.